As imaging technology continues to evolve, the nuances of capturing and interpreting visual data become increasingly important.
One such nuance often left unexplored is the use of IR-cut filters, especially in embedded vision systems. IR-cut filters ensure that embedded cameras can capture image data properly during the daytime.
This deep dive into the IR-cut filter will provide insight into its importance, applications, and workings in embedded vision systems.
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a professional in the industry, or just curious about modern imaging technology – this exploration promises to offer something for everyone.
Let’s delve deep into this intriguing technology.
Understanding the IR Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is a wide range of wavelengths, encompassing everything from the shortest gamma rays to the longest radio waves.
Within this vast spectrum lies the world of the infrared (IR) spectrum. Positioned between the visible light spectrum and the microwave region, the IR spectrum is useful in imaging techniques and various scientific and medical applications.
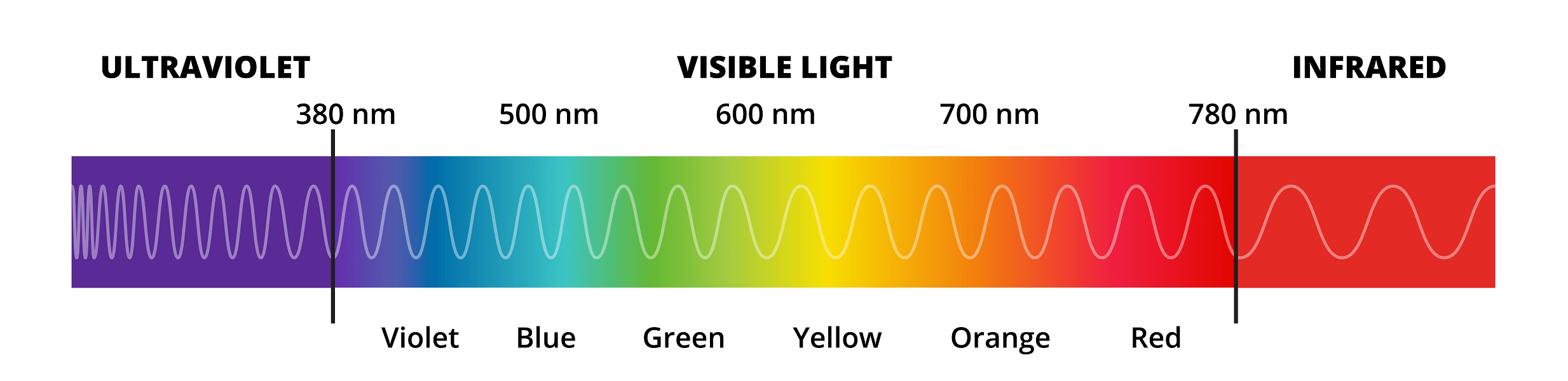
The Infrared Spectrum
A Few Basic Concepts Related to the IR Spectrum
This post primarily concerns CMOS image sensors, which are inherently sensitive in various degrees to portions of the NIR spectrum, but the IR spectrum is much larger and can be divided into distinct regions, each with its own characteristics and practical applications:
- Near-Infrared (NIR, 700-1400 nm): Just beyond the range of human vision, NIR finds valuable use in electronics, particularly in remote controls. By harnessing NIR, you can easily communicate between various electronic devices, making control more
convenient and efficient. - Short-Wavelength Infrared (SWIR, 1400-3000 nm): With a reflective nature, SWIR plays a vital role in satellite imaging, enabling the detection of moisture and the differentiation between water bodies and dry areas. Using SWIR technology, you can gather accurate and valuable information for various applications.
- Mid-wavelength infrared (MWIR, 3000-8000 nm): Sensitive to common terrestrial temperatures, MWIR is extensively employed in night vision devices. By detecting emitted heat, MWIR plays a critical role in enhancing visibility in low-light conditions, ensuring the safety and security of various operations.
- Long-Wavelength Infrared (LWIR, 8000-15000 nm): Operating on a thermal basis, LWIR is what is detected by thermal imaging cameras. This technology is widely used in industries such as firefighting, security systems, and various industrial applications. By utilizing LWIR, you gain the ability to detect infrared radiation emitted by objects, providing crucial insights and enabling informed decision-making.
- Far Infrared (FIR, 15000 nm-1 mm): FIR is associated with thermal radiation and has found significant application in therapeutic infrared saunas. By leveraging FIR technology, these saunas provide soothing and beneficial heat through absorbed infrared light, promoting relaxation and well-being.
What is an IR-Cut Filter?
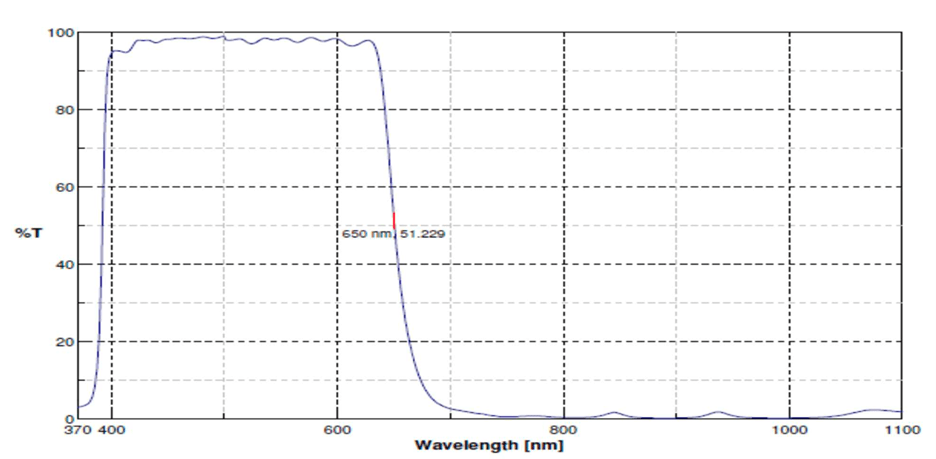
Typical 650nm IR-Cut
Nearly all CMOS image sensors have at least some sensitivity in the near-infrared spectrum.
Because of this, an indispensable component in modern imaging technology, the IR-cut filter, also called an infrared cut-off filter, can block infrared (IR) light while permitting visible light to pass through.
It serves as a notch filter, blocking longer wavelengths such as IR from being transmitted through to the sensor, as well as shorter wavelengths such as UV.
The IR-cut filter serves a vital purpose in embedded cameras by filtering invisible infrared radiation, ensuring only visible light reaches the sensor.
Why is an IR-Cut Filter Important?
IR-cut filters are a game-changer in embedded vision systems primarily because of two reasons:
- Unadulterated color accuracy: Digital camera sensors are prone to sensitivity to IR light, which can distort the true colors they perceive. In scenarios where infrared enters the camera lens, it can result in a reddish or washed-out effect, particularly in daylight. Implementing an IR-cut filter ensures that exclusively visible light reaches the camera sensor, thereby preserving the accurate representation of colors in both photos and videos.
- Seamless transition between day and night: Numerous security cameras have the day/night mode feature. During daytime operations, an IR-cut filter is placed in the optical path, facilitating clear and precise color capture. This filter disengages as the camera transitions to night mode, allowing IR light to permeate. This enables the camera to excel in capturing images in the dark, often working in conjunction with IR LEDs that emit infrared light.
How does an IR-Cut Filter Function?
The IR-cut filter effectively operates by either reflecting or absorbing infrared radiation. Typically composed of specialized materials with distinct transmissive or reflective properties, the filter is positioned before the camera’s sensor. Depending on the camera’s design, it may either undergo mechanical movement in or out of the light path for cameras equipped with a day/night functionality, or it may remain fixed in place for cameras lacking night vision capabilities. Depending on the lens assembly and sensor, the filter may be a coating on the lens, or it might be a cover glass placed directly above the sensor.
Working Principle of IR-Cut Filter
As mentioned, the IR-cut filter blocks infrared light from reaching the camera sensor while enabling visible light to pass through. Let’s delve deeper into the intricacies of its working principle:
- Composition and Construction: The IR-cut filter is meticulously crafted using specially designed optical glasses or glass coated with specific materials. These materials are precisely engineered to possess distinct reflective or absorptive properties concerning infrared light.
- Reflecting or absorbing Infrared light: The specialized materials employed in the filter’s construction either absorb or reflect infrared light, redirecting it away from the camera’s sensor. This selective filtration allows only visible light within the wavelength of 400 to 700 nm to reach the sensor, resulting in exceptionally clear and accurate images.
- Fixed vs. Switchable filters:
Fixed Filters: These filters are permanently positioned before the camera’s sensor, consistently blocking infrared light. They are well-suited for applications where any interference caused by infrared light is undesirable and sufficient visible light is available for imaging.
Switchable Filters: Possessing greater versatility, switchable IR-cut filters can mechanically move in and out of the camera’s optical path. This adaptability allows for dual-mode operation:
Day mode: During daylight or well-lit conditions, the filter is engaged. This is extremely helpful in systems like smart traffic devices where the camera is often exposed to bright sunlight.
Night mode: In low-light or nighttime scenarios, the filter disengages. This switching is done using a mechanical switch that removes the ‘IR curtain’ in front of the camera. When combined with infrared illumination, the camera captures sharper and more detailed black-and-white images by leveraging the infrared light to illuminate the scene.
How to Choose an IR-Cut Filter for Your Cameras
Selecting the right IR-cut filter is crucial for optimal camera performance. Consider the following factors:
- Spectral Range: Determine the range of wavelengths you want to block or pass through.
- Transmission: Ensure that the filter doesn’t significantly reduce the amount of visible light reaching the sensor.
- Switching Mechanism: Opt for switchable filters if you require both day and night imaging.
- Size and Shape: Match the filter’s physical dimensions with your camera’s requirements.
Always check manufacturers’ specifications and, if possible, test the filter with your camera before finalizing your choice.

Embedded Vision Applications of IR-Cut Filters
Embedded vision systems have revolutionized how machines perceive and interact with their surroundings, finding applications across diverse industries. At the heart of many of these systems (especially those operating both day and night), the IR-cut filter is pivotal in enhancing image quality and providing accurate visual data. Here are some key areas where the IR-cut filter is crucial:
Security and Surveillance
In modern security cameras that operate 24/7, the IR-cut filter ensures that daytime images are free from color distortions caused by infrared light.
At night, cameras with switchable filters disengage the filter to leverage infrared illumination, capturing clear images even in complete darkness.
Automotive Industry
Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) rely on embedded vision to detect obstacles, lane markings, and other vehicles. IR-cut filters are vital to prevent overwhelming camera sensors with infrared light, particularly during daytime driving, ensuring safer navigation.

Entertainment and Augmented Reality
For precision applications like motion capture, cameras equipped with IR-cut filters ensure precise data capturing by filtering out unwanted infrared interference, enabling accurate tracking of movements.
Industrial Inspection
In automated manufacturing lines with essential visual inspection processes, embedded vision systems with IR-cut filters guarantee accurate color representation, resulting in more reliable quality checks and improved production efficiency.
They also enable imaging in the IR or NIR spectrum by removing the filter when needed. This helps detect fissures and dents that might be challenging to view under visible light.
Healthcare and Medical Imaging
Certain medical imaging applications heavily rely on visual data, which might need the removal of light in the IR spectrum. An example of a medical application that deploys an IR-cut filter is patient monitoring. In patient monitoring systems, IR-cut filters enable 24×7 monitoring of patients without affecting the image quality.
TechNexion: Near-IR Enhanced Cameras for Embedded Vision Applications
As embedded vision grows in various industries, the importance of technologies like the IR-cut filter will only become more pronounced.
Whether for security, automotive applications, or entertainment, capturing accurate, clear images is paramount, and it is needless to say that IR-cut filters have been an important part of this.
TechNexion has a comprehensive range of specialized cameras specially designed to meet the needs of the embedded vision sector.
Our near-infrared (NIR) enhanced cameras are ideal for low-light conditions, making them perfect for nighttime surveillance or applications where light is unpredictable. Our NIR cameras can be integrated with IR-cut filters and IR LED lights, making them perfect for dual-mode cameras that need to operate during the day and the night.
Related Products
- Understanding the IR Spectrum
- A Few Basic Concepts Related to the IR Spectrum
- What is an IR-Cut Filter?
- Why is an IR-Cut Filter Important?
- How does an IR-Cut Filter Function?
- Working Principle of IR-Cut Filter
- How to Choose an IR-Cut Filter for Your Cameras
- Embedded Vision Applications of IR-Cut Filters
- Security and Surveillance
- Automotive Industry
- Entertainment and Augmented Reality
- Industrial Inspection
- Healthcare and Medical Imaging
- TechNexion: Near-IR Enhanced Cameras for Embedded Vision Applications
- Related Products
Get a Quote
Fill out the details below and one of our representatives will contact you shortly.