An Image Signal Processor (ISP) is a key camera component that helps achieve the desired output quality in imaging systems. It is the ISP that converts raw images delivered by an image sensor into a usable form, which can then be used by the embedded vision system for various tasks.
Most sensors are relatively simple devices. However, camera systems have to perform a sophisticated set of image processing tasks. They also need a few control systems for managing gain, exposure, and in some cases focus, in order to make them functional.
For example, imagine an automated liquid handling system used in a laboratory to automatically identify the sample in a test tube based on the color of its cap. This requires the camera system to capture and identify colors. This will be possible only with the help of an ISP.
In this article, let us understand what an ISP is, its importance and functions in imaging systems, its types, and much more.
What is an ISP?
An ISP or Image Signal Processor is a dedicated processor in an imaging system that is responsible for processing images. Along with the hardware-based processing, different types of software enhancements are also done to ensure you get all the imaging parameters like contrast, gain, sharpness, gamma, etc., right.
The process of using an ISP to achieve the desired image quality is called ISP tuning. This is a critical step in camera integration since choosing a camera with the right set of features alone is not enough. You need to make sure that you are able to customize the camera to meet the quality requirements of the end application.
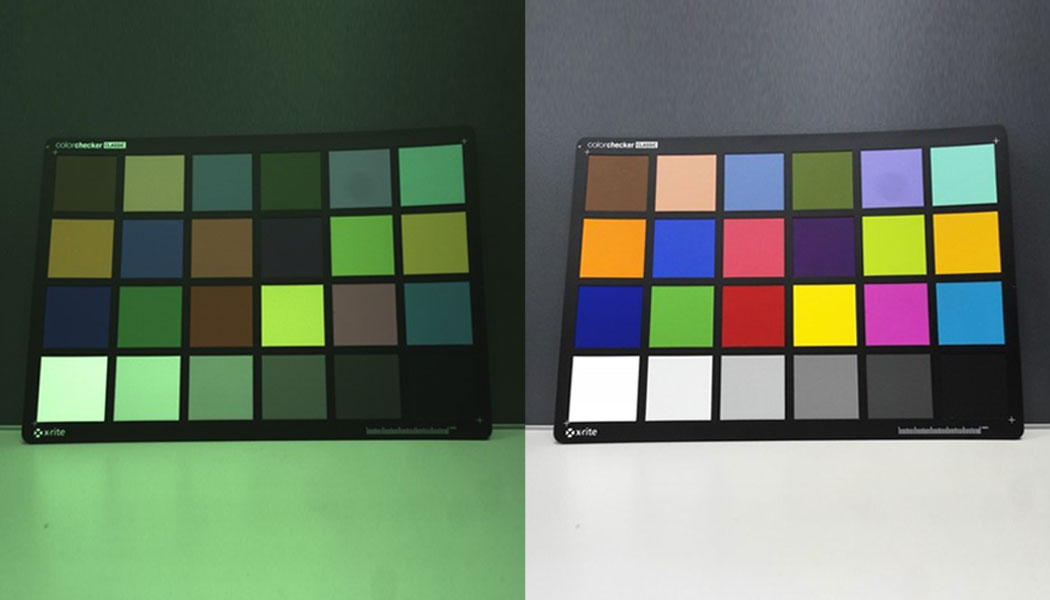

A comparison of images without and with ISP

A harvesting robot
Let us understand this through an example.
Consider a harvesting robot used in agriculture for plucking fruits and vegetables.
The robot uses embedded cameras and computer vision to identify the color of fruits and vegetables. This is one of the parameters based on which the robot determines whether the produce is ready to be harvested. In this case, color accuracy is of utmost importance since it feeds the AI algorithm the necessary data to take an action (whether to harvest or not). Hence, the performance of the ISP becomes critical in an application like this.
What are the functions of an ISP in a camera system?
An ISP performs the following functions in a camera system:
- Image Capture and Image Signal Processing (ISP) Initialization:
An image sensor captures raw images. These images are in an unprocessed format, typically using a Bayer pattern which contains information for red, green, and blue color channels. It is the ISP that processes the raw images received from the sensor. For example, most TechNexion cameras come with the AR series of sensors from Onsemi. In these camera modules, the AR sensor captures images, and these images are processed using the AP1302 ISP. - Demosaicing:
Demosaicing is the process of converting the raw Bayer-patterned image data into a full-color image. This process fills in the missing color information for each pixel by interpreting the surrounding pixels. - Color Correction:
The ISP adjusts the colors in the image to ensure they are accurate and match real-world colors. This step corrects any color imbalances that may have occurred during the capture process. - Noise Reduction:
The ISP applies noise reduction techniques to the image to minimize any unwanted artifacts or ‘noise’ that can distort the quality of the image, especially in low-light conditions. - Auto Exposure (AE):
The ISP automatically adjusts the brightness of the image by changing the exposure settings based on the amount of light in the scene. This ensures that the image is neither too dark nor too bright. This is extremely important in vision systems that operate in varying lighting conditions. A smart traffic system that operates during the day and at night is a great example.

MIPI-CSI2 Sensor onsemi AR0234 2MP Full-HD Global Shutter with ISP
TEVS-AR0234
- onsemi AR0234 2.3MP global shutter image sensor with ISP
- Captures high-speed dynamic targets clearly within an ultra-short exposure time
- Convenient S-Mount (M12) interchangeable lens
- VizionViewer™ configuration utility
- VizionSDK for custom development
- Auto White Balance (AWB):
The ISP automatically corrects the white balance of the image, adjusting for different lighting conditions so that the colors appear natural. This step ensures that whites look white and other colors are rendered correctly. An ISP performs white balancing by taking white as the reference color. - Image :
The ISP performs various image enhancement functions such as sharpening, contrast adjustment, and gamma correction to improve the overall quality and clarity of the image. This ensures that the output images can be properly analyzed by humans or computer vision software. - Output:
The ISP also provides the output image in a format that can be used by the system, such as a display or for further image analysis by an embedded vision system.
Variants of image signal processors
ISPs come in three variants – on-sensor ISP, on-SoC ISP, and external ISP. Let us look at each of them in detail in this section.
1. On-Sensor ISP
An on-sensor ISP, as the term suggests, is directly integrated into the image sensor chip, allowing the data output from the sensor to be processed internally. Since the ISP and sensor are combined on the same chip, data transmission is more efficient, and latency is reduced.
Some of the key advantages of using an on-sensor ISP include:
- Simplified system design: Since the ISP comes integrated with the sensor, you don’t have to worry about any other design considerations.
- Reduced dependence on external ISPs: With an on-sensor ISP, if the necessary image processing needs are met, an external ISP is not required.
- Low power consumption: With fewer components, a camera module with an on-sensor ISP significantly lowers the power consumption of the system.
- Low costs: On-sensor ISPs can lower the total cost since you don’t have to integrate additional components for image processing.
- Enhanced data security and privacy: With increasing data security concerns, using an on-sensor ISP can be an added advantage since all the processing is done on the sensor itself.
2. On-SoC ISP
An on-SoC ISP is integrated into the System on Chip (SoC) and works alongside other processing units like the CPU, GPU, and DSP to form a complete solution. Image data is transmitted from the sensor to the ISP within the SoC for processing, and then further processed or stored by other modules.
Below are the major advantages of using an on-SoC ISP:
- Powerful image processing: On-SoC ISPs can handle more complex image processing tasks compared to an on-sensor ISP.
- Better system performance and responsiveness: As part of the SoC, the ISP can work seamlessly with other processing units, improving overall system performance and responsiveness.
3. External ISP
An external ISP is a standalone chip that is not integrated into the sensor or SoC. The sensor transmits image data to the external ISP for processing, and the processed data is then sent to the main processor for further processing or storage.
The advantages of an external ISP include:
- Robust processing capabilities: External ISPs come with the ability to handle complex and custom image processing tasks.
- More flexibility: The advanced processing capabilities allow product developers to build systems that have nuanced processing needs.
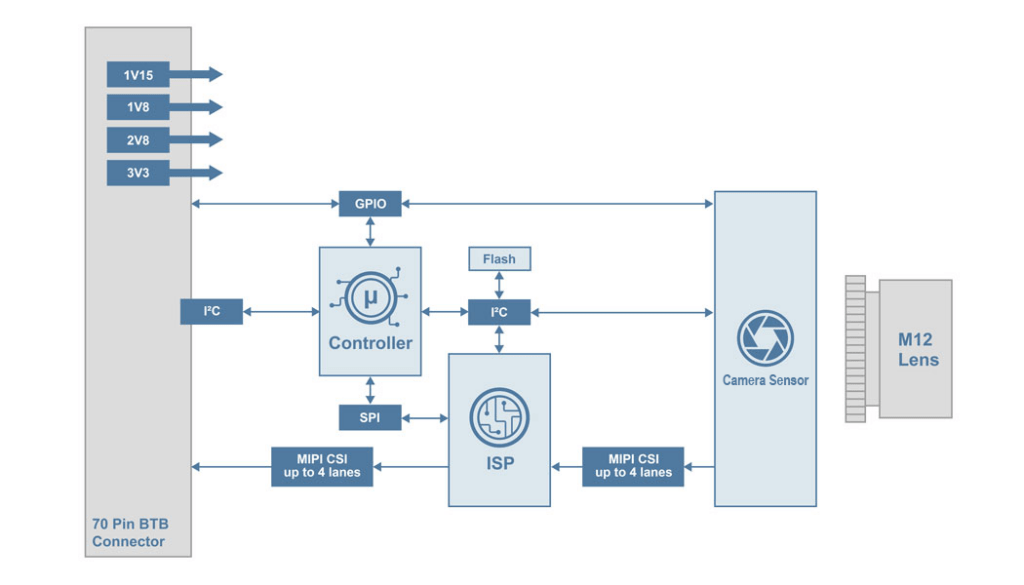
ISP Block Diagram
How to choose an ISP for your embedded vision system?
Among the three types of ISPs discussed in the previous section, you need to choose the right one for your vision system by considering parameters such as processing needs, ease of integration, and cost.
If you have customized image processing needs, an external ISP is the best choice. If simplicity of design and low cost are your biggest considerations, an on-sensor ISP would work as long as the image processing needs are simple. On-SoC ISPs kind of lie in between with the ability to handle complex processing tasks while seamlessly integrating with other processing units.
TechNexion – making camera integration easy
TechNexion offers a wide range of embedded vision solutions such as high-resolution cameras, global shutter cameras, HDR cameras, NIR cameras, etc. While our cameras come with the necessary features required for your embedded vision system, we make integration easy by using the same driver for all our camera solutions. In addition, TechNexion also offers VizionViewer, a cross-platform camera software for video streaming and image capturing. It is compatible with x86 platforms (such as Windows and Linux) as well as embedded platforms (such as TI, NVIDIA, and NXP), making camera integration a hassle-free process for product developers.
You can learn more about our embedded vision solutions here.



