Shopping has seen various transformations over the years. The internet opened opportunities to take it online. That’s what Amazon capitalized on in the mid-90s to make shopping convenient and easy for millions around the world.
As we move into the AI era, the next revolution in shopping is here – autonomous shopping. Autonomous shopping is the process of reducing manual involvement in shopping by automating tasks such as product logging, billing, and checkout, allowing the shopper to simply depart the store with the purchase occurring seamlessly without human cashiers. This requires multiple technologies to work together including:
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms
- AI-enabled cameras
- A software or application where the data can be stored and shopping transactions can be performed

Embedded vision comes into play by helping autonomous shopping systems like smart carts and smart checkout devices identify products without the help of retail staff. They also assist in inventory management by enabling automated tracking of retail shelves – thereby making sure that the store location is stocked so that shoppers get what they want all the time.
In this blog post, we explore the world of autonomous shopping through the lens of embedded vision. We will learn in detail about the different types of camera-enabled autonomous shopping systems, how cameras help them ‘see’, the different features you need to consider while selecting a camera for autonomous shopping systems, and much more.
What are Autonomous Shopping Systems?
Camera-based autonomous shopping systems capture images and videos to help identify objects in the shopping cart to automatically add them to the billing software. The customer-facing side of the application can then be used to make the payment. The payment process is also eased by using a single step of authentication in most cases.
Now, how does the device identify objects automatically?
That’s where AI/ML-based algorithms come in. The device uses trained computer vision and object recognition models to analyze images captured by embedded cameras to identify fruits, vegetables, or any other shopping item for that matter.
Different Types of Autonomous Shopping Systems

Autonomous shopping systems primarily come in 3 forms:
- Automated checkout: Automated checkout devices are placed at the checkout counter where the products can be placed in the field of view of the cameras for identification.
- Smart cart devices: These include cameras and a processing unit placed in the shopping cart or trolley itself.
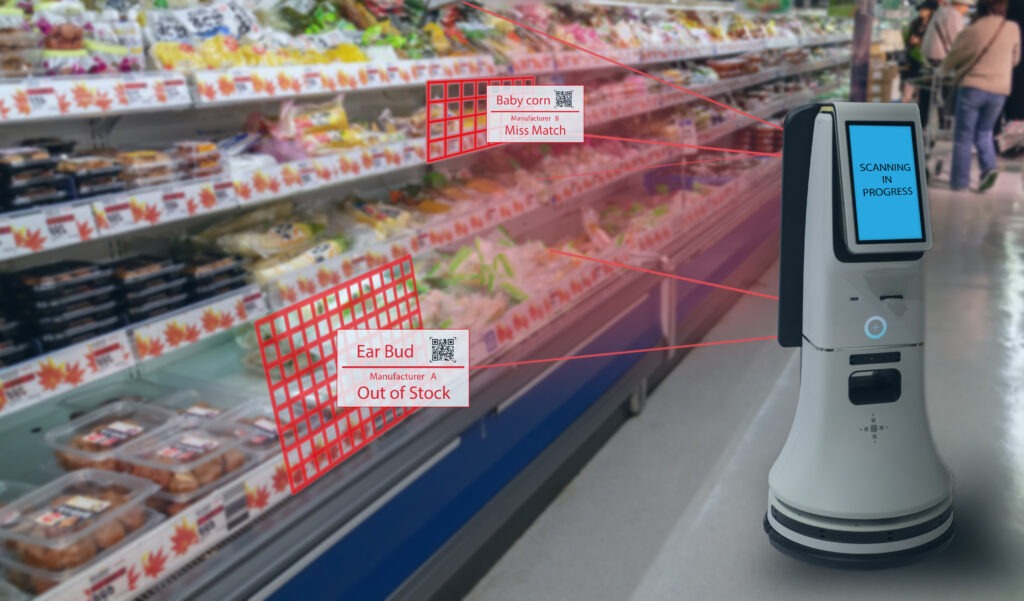
- Roof-mounted cameras/shelf monitoring cameras: These are camera units placed on the roof, walls, or retail shelves for inventory tracking, object identification, and people counting.
In all three cases, cameras capture images of the items while the AI/ML algorithms analyze and accurately identify them.
How do Cameras, Processors, and AI Algorithms Work Together to Identify Objects?
As mentioned, embedded cameras are the eyes of autonomous shopping systems. They capture the necessary images and feed them to the processing unit which acts as the brain of the device. The processor must be capable of handling the bandwidth required for image processing and running the object identification algorithm.
Some of the popular processing platforms that can manage AI workloads include NVIDIA Jetson, TI Jacinto TDA4VM, and NXP i.MX8.
Object identification can be carried out in two different ways:
- By reading barcodes: This is the simpler of the two methods where the camera reads the barcode on the item on the shelf, cart, or checkout counter.
- By using computer vision to identify objects based on their color, shape, size, texture, etc.
Multiple cameras are usually used to capture images of the object from different angles to make sure the barcode or the object is fully captured. This ensures that the AI algorithm has enough image data to identify objects with high accuracy.
In addition to using image data, other sensors are used to capture information such as item weight. This is compared with the expected weight of an identified product to ensure additional accuracy.
Single-camera vs. Multi-camera Systems in Autonomous Shopping
Object recognition is often challenging to carry out without capturing the image of an object from multiple points of view. For this reason, most autonomous shopping systems use multiple cameras.
For instance, consider a smart cart system where the customer drops items as he or she does shopping. The camera system identifies the items on the go as they are dropped into the cart.
Whether the identification is done through barcode reading or computer vision, one perspective will not give the complete view of the object. Smart carts often come equipped with a minimum of 3 cameras so that a 360-degree view of the object can be obtained.
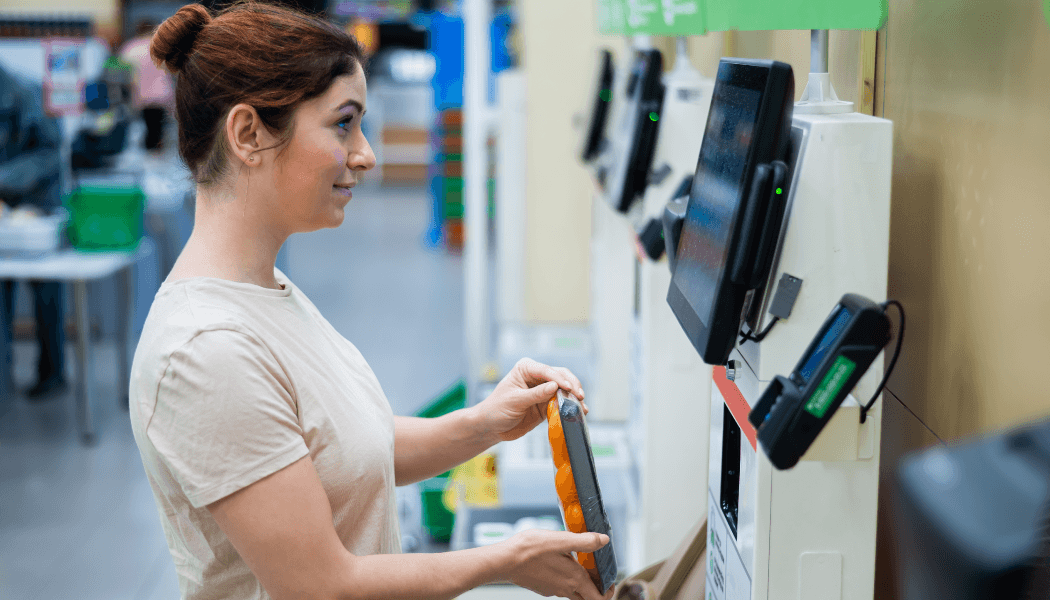

Single-camera systems are used only when there is some form of guided recognition or personnel involvement. For example, if the shopper is always instructed to keep the items in a designated area at the checkout counter that falls under the field of view of the camera (that too with the right orientation), object recognition can be carried out using a single camera. Another example would be manual barcode scanning, in which the user is instructed by the cart software to hold a particular item in front of a high-resolution camera so that its barcode can be captured and scanned.
Also read: Single Camera vs. Multi Camera – Similarities, Differences, and Applications
How to Select a Camera for Autonomous Shopping

We briefly touched upon choosing between single and multiple cameras. In addition to covering a 360-degree view, another reason why you would want to use multiple cameras is to avoid lens distortions that tend to occur at high FOV (Field Of View) values.
Apart from the number of cameras, following are the factors you need to consider while choosing embedded camera modules for your autonomous shopping system:
- Resolution & frame rate
- Chroma
- Shutter type
- Field of view
- Sensitivity and dynamic range
- Distance of transmission
- Processor compatibility
Resolution & Frame Rate
For autonomous shopping systems, very high resolution is rarely required. A resolution of 5 MP is enough in most cases. This is because object recognition can be done at this resolution if the camera meets other quality criteria.
When it comes to frame rate, a high frame rate (up to 120 fps) might be required since the cameras must capture images without blur as the items are dropped into the shopping cart.
Chroma
If object recognition is done purely based on barcodes that come in black and white, a monochrome camera will suffice. Given that monochrome cameras tend to offer higher sensitivity compared to color cameras, they are a better alternative in such a scenario.
However, modern autonomous shopping systems are designed to identify objects based on color, color camera is required here.
Shutter Type
Most smart carts or smart checkout systems will be able to function properly using a rolling shutter camera with a high frame rate. Given that global shutter cameras are costlier, they are recommended only if shutter artifacts are observed in the output image.
Field of View
The field of view a single camera can cover determines the number of cameras you need to use in an autonomous shopping system. Usually, a combination of 3 to 4 cameras does the job. It is always recommended to test the camera system by integrating it into the autonomous shopping device to make sure the number of cameras you have chosen is appropriate.
Sensitivity and Dynamic Range
While most retail stores are well lit, there could be situations where adequate light is not available. In these scenarios, having a camera with high sensitivity and dynamic range helps. This is because they can operate in wide luminosity levels.
Distance of Transmission
The choice of interface in an embedded camera solution used in autonomous shopping systems is determined primarily by two factors:
- The bandwidth to be handled
- Distance of transmission
Given that cameras in autonomous shopping systems are often placed at a distance of 1 to 2 meters from the processor, a SerDes interface may be a better choice compared to USB (direct MIPI doesn’t stand a chance anyway given its maximum distance of transmission of 30 cm). A SerDes interface like FPD-Link III can offer a bandwidth of more than 4 Gbps. Long-distance transmission and the ability to offer high bandwidth make it a good choice for any kind of autonomous shopping system.
Processor Compatibility
The processor you choose will depend on the AI workload the system has to handle. From NVIDIA to Texas Instruments and NXP, there is a wide variety of options to choose from. To ensure smooth integration, choose a camera that is compatible with the processing platform you are using.
The Future of Camera-enabled Autonomous Shopping
According to Verified Market Research, the Global Retail Automation Market size was valued at USD 13.97 Billion in 2020 and is projected to reach USD 31.81 Billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 10.94% from 2021 to 2028. A part of this growth will be contributed by autonomous shopping systems. As demand increases for an Amazon Go-like experience, the need for a camera and AI-based autonomous shopping systems is only going to rise.
This will in turn fuel further research into camera technology and computer vision –increasing the accuracy and speed of smart carts, smart checkout, and shelf monitoring systems in retail stores and reducing their cost. The focus on offering a personalized shopping experience to customers leveraging data and AI is also likely to increase. Cameras will play a role here by helping to analyze the behavior of shoppers while they are in the store. This data will be fed into the software to personalize the overall shopping journey for customers.
TechNexion: Cameras for Next-generation Autonomous Shopping Systems
Autonomous shopping is one of the focus areas at TechNexion where we build camera solutions that can be readily integrated with any autonomous shopping system. We also help our customers with integration challenges. To learn more about our camera solutions, visit the embedded vision page.
Related Products
- What are Autonomous Shopping Systems?
- Different Types of Autonomous Shopping Systems
- How do Cameras, Processors, and AI Algorithms Work Together to Identify Objects?
- Single-camera vs. Multi-camera Systems in Autonomous Shopping
- How to Select a Camera for Autonomous Shopping
- Resolution & Frame Rate
- Chroma
- Shutter Type
- Field of View
- Sensitivity and Dynamic Range
- Distance of Transmission
- Processor Compatibility
- The Future of Camera-enabled Autonomous Shopping
- TechNexion: Cameras for Next-generation Autonomous Shopping Systems
- Related Products
Get a Quote
Fill out the details below and one of our representatives will contact you shortly.