Embedded vision is revolutionizing how we perceive the world around us, entering a period of transformative innovation. This cutting-edge technology has become a catalyst for change across all industries, stretching the boundaries of what was once considered possible. Amid this revolutionary surge of progress, agriculture stands out as a key industry that is being transformed by the force of embedded vision.
Before cameras started finding their way into agricultural practices, precision farming was mostly about taking manual measurements and performing analysis to understand the status of crops and take action accordingly. For example, by applying fertilizers, removing weeds, and using the right amount of water – all done manually.

What embedded vision makes possible is to automate the entire lifecycle of precision farming activities. Embedded vision systems, consisting of camera modules and embedded processors, are used in agricultural robots, tractors, and drones to monitor crops, detect pests and non-beneficial plants (weeds), perform soil analysis, and much more. Furthermore, with artificial intelligence making giant strides, embedded vision is only getting better at supporting precision farming.
What is Embedded Vision?
Embedded vision is the integration of computer vision capabilities into embedded systems, allowing machines to “see” and interpret visual data. It performs real-time analysis and interpretation of images & videos using camera modules, processors, and AI algorithms.
One of the main advantages of embedded vision is the ability to process visual data directly on the device itself, without cloud connectivity or external processing. This processing on the device is convenient because it enables real-time analysis and decision-making. It eliminates the requirement for continuous data transmission to the cloud, thereby decreasing latency and reducing response time. This reduces operational expenses related to data transmission and cloud processing.
What is Precision Farming?
Precision farming, also known as precision agriculture or smart farming, is a technique that employs technology and data to optimize agricultural practices and increase crop yield. It uses satellite imagery, GPS, sensors, cameras, and data analytics to collect information about the state of the soil, weather patterns, the condition of crops, and other relevant factors. This data is subsequently utilized for making targeted irrigation, fertilization, pest control, and farm management decisions. Increased agricultural productivity, resource optimization, cost savings, environmental sustainability, and intelligent decision-making are all benefits of precision farming.
How Embedded Vision is Changing Precision Farming
Embedded vision is significantly transforming precision farming by harnessing the power of cameras and computer vision algorithms across various aspects of agricultural practices. Here are a few examples:
Crop Monitoring
Cameras play a vital role in monitoring crop growth in precision farming. By capturing images or videos, data are used to measure and track the general progress of crops. Cameras mounted on drones or robots can be used to capture images in both visible and near-infrared (NIR) spectra to measure the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI). NDVI analysis provides valuable insights into crop health, identifying areas of concern and enabling targeted interventions.

Planting
Cameras integrated with robots and autonomous tractors enable the precise planting of trees and crops. By using computer vision algorithms, cameras provide real-time feedback on seed placement, ensuring accurate spacing, alignment, and optimal soil coverage. This ensures consistent and uniform growth, leading to improved crop establishment and higher yields.
Plowing
Embedded vision systems equipped with cameras can improve plowing processes. Cameras capture images to identify the exact location where plowing is required. Computer vision algorithms analyze these images to guide automated plowing, ensuring precise and efficient soil preparation.
This is done using a combination of RGB (color) and depth cameras. While RGB cameras capture images to help understand soil conditions, depth cameras (often powered by stereo or time of flight technologies) help tractors to precisely determine the location and depth of plowing. Depth cameras also help in navigation, obstacle detection, and localization in tractors and robots.
Harvesting
Cameras and embedded vision technologies greatly enhance the harvesting process. Cameras capture images of fruits and vegetables, and AI/ML algorithms analyze these images to determine ripeness. Based on the analysis, robots and autonomous systems can selectively harvest ripe crops, optimizing efficiency, reducing labor requirements, and improving the quality of harvested produce. Automated harvesting can be done in many different domains: open agricultural lands, greenhouses, and vertical farming.
Weed and Bug Detection
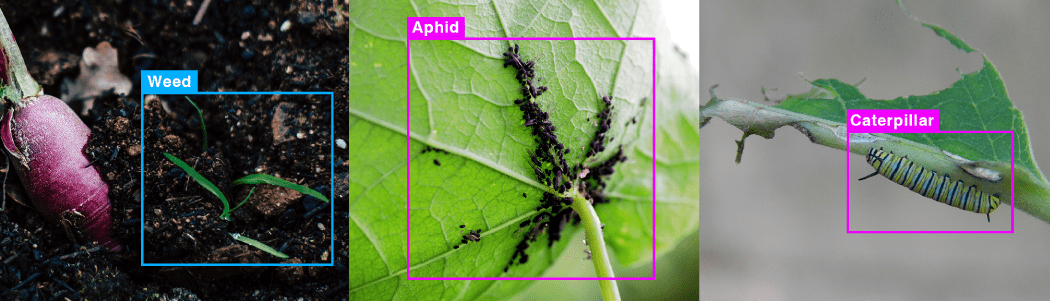
Cameras are used to capture images of vegetation and crops, and embedded vision systems, employing AI/ML algorithms, can be used to detect and differentiate between crops and beneficial plants from other things that are non-beneficial such as weeds and bugs. With this information, robots and tractors can precisely remove weeds or pests and apply fertilizers, reducing the need for chemical interventions and ensuring the health of crops.
Soil Analysis
By analyzing images captured by cameras, computer vision algorithms can estimate soil properties such as texture and moisture content. Robots and drones equipped with cameras can capture high-resolution images of the soil, which are then processed to provide valuable insights for optimal soil management, irrigation, and fertilization practices.
Vertical Farming
Similar to crop monitoring in traditional farming, in vertical farming. cameras are employed to measure and monitor crop growth… By capturing images of vertically stacked crops, embedded vision systems assist in tracking growth patterns, identifying potential issues, and optimizing environmental conditions for maximum yield.
Cameras used for monitoring in vertical farming environments are usually static and are placed in the room in a way that they can view the entire vegetation. Mobile robots can also be used in vertical farming for crop monitoring, carrying materials from one place to the other, bug & weed detection, and harvesting.
Machines and Devices Using Cameras in Precision Farming
Cameras in precision farming are used in a variety of machines that allow them to work and integrate into agricultural activities. The following machines come integrated with cameras for precision farming tasks:
Robots
Robots are important in automating many agricultural tasks. They have cameras to help in crop monitoring, harvesting, automatic weeding, and soil analysis.
Harvesting robots use images, video, and AI/ML algorithms to detect ripe fruits and vegetables, and facilitate accurate and efficient harvesting.
Cameras are used in automated weeders to identify weeds and execute targeted weed removal. Soil analyzers with cameras record images for study and provide vital information about soil qualities.
Robotic arms, which often come fitted on harvesting robots and tractors, assist in various agricultural tasks, such as planting and picking & placing.

Drones
Drones are gaining popularity in precision agriculture due to their capacity to cover vast areas and provide aerial perspectives. Drones equipped with cameras are used for crop monitoring to calculate the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI)detecting animal intrusion, Identifying soil moisture levels, and observing the pollination of flowering plants.
Tractors
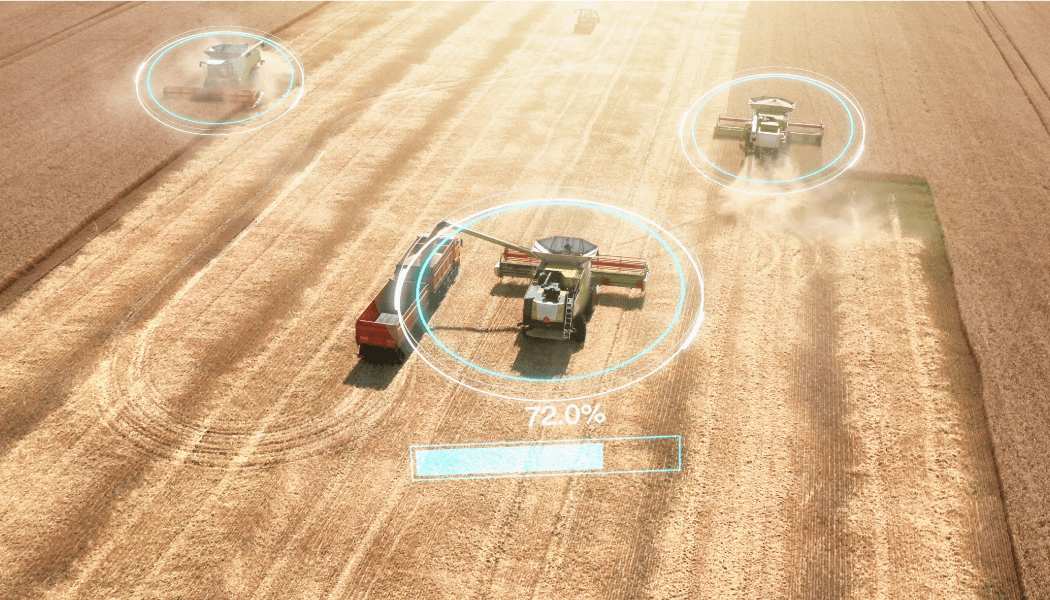
Tractors with cameras mounted on them can perform automatic plowing, find weeds and bugs, and distribute fertilizer. Cameras are used by automated plowing systems to pinpoint the exact areas that need plowing, guaranteeing precision and effectiveness. Tractor cameras assist in differentiating between crops, weeds, and pests, enabling targeted treatments. In addition, cameras on tractors facilitate the precise administration of fertilizer based on crop requirements, thereby reducing waste and optimizing resources.
Another important way in which cameras play a role in tractors is autonomous navigation. With the help of depth cameras, tractors can detect obstacles, localize themselves in their environment, and move from one place to the other by mapping the path between them.
TechNexion Embedded Vision Cameras: Changing the Way Farming is Done
We at TechNexion offer embedded vision camera solutions specifically designed for various industries, including agriculture. Our camera solutions are changing the way farming is done by providing advanced imaging capabilities for precision agriculture. Our embedded vision cameras are equipped with high-quality image sensors to capture crisp and detailed images. This guarantees accurate crop, pest, soil, and other agricultural aspect monitoring and analysis.
Check out our embedded vision solutions here.
TechNexion’s cameras are compact and durable, making them ideal for challenging agricultural applications. We provide easy integration with a wide range of devices, including drones, robots, tractors, and other precision agricultural equipment. They are also compatible with popular processing platforms like NVIDIA Jetson, and NXP i.MX8, and TI Jacinto TDA4VM, and connect to them using the USB3, MIPI CSI-2, and FPD-Link III interfaces.
We also provide customization options to adapt camera systems to particular agricultural needs. These include lens changes, IP68 enclosure, helping with complete system design, and more. Book a session with one of our camera consultants to learn more about how we can help you build your next vision product.
Related Products
- What is Embedded Vision?
- What is Precision Farming?
- How Embedded Vision is Changing Precision Farming
- Crop Monitoring
- Planting
- Plowing
- Harvesting
- Weed and Bug Detection
- Soil Analysis
- Vertical Farming
- Machines and Devices Using Cameras in Precision Farming
- Robots
- Drones
- Tractors
- TechNexion Embedded Vision Cameras: Changing the Way Farming is Done
- Related Products
Get a Quote
Fill out the details below and one of our representatives will contact you shortly.