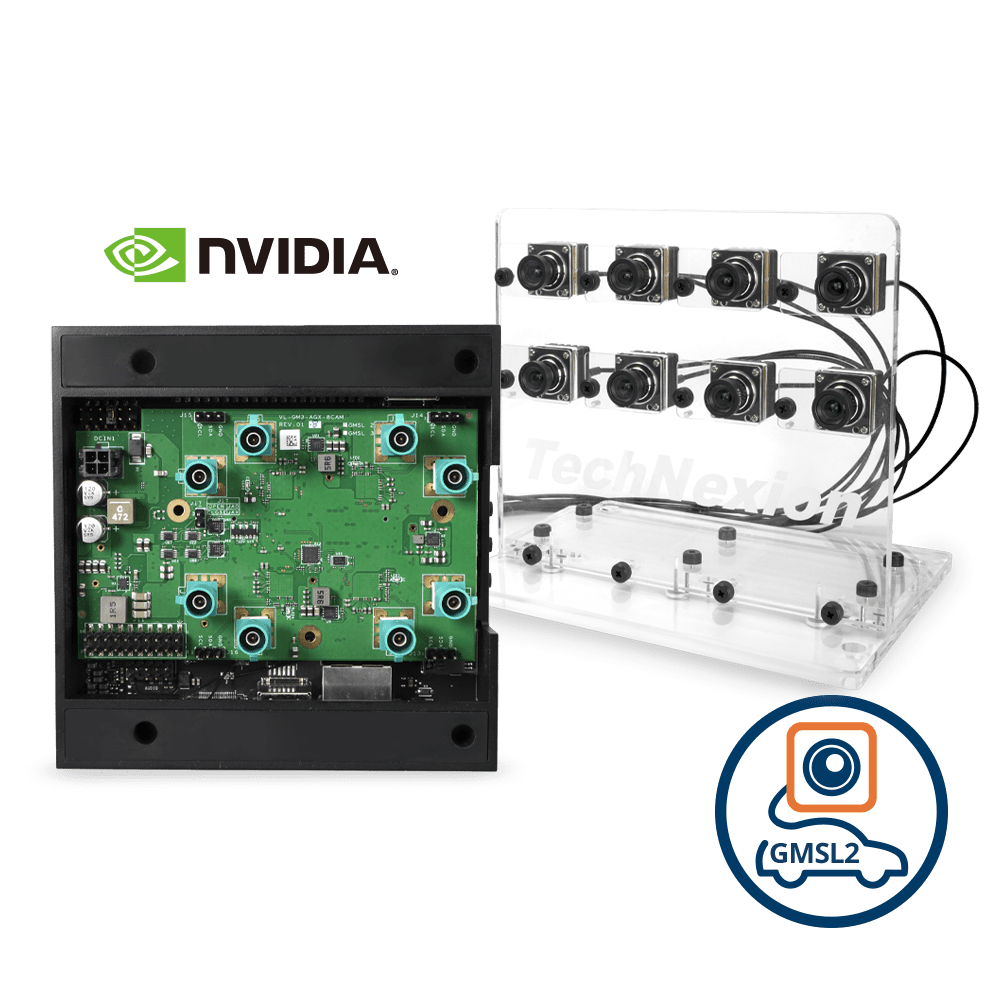
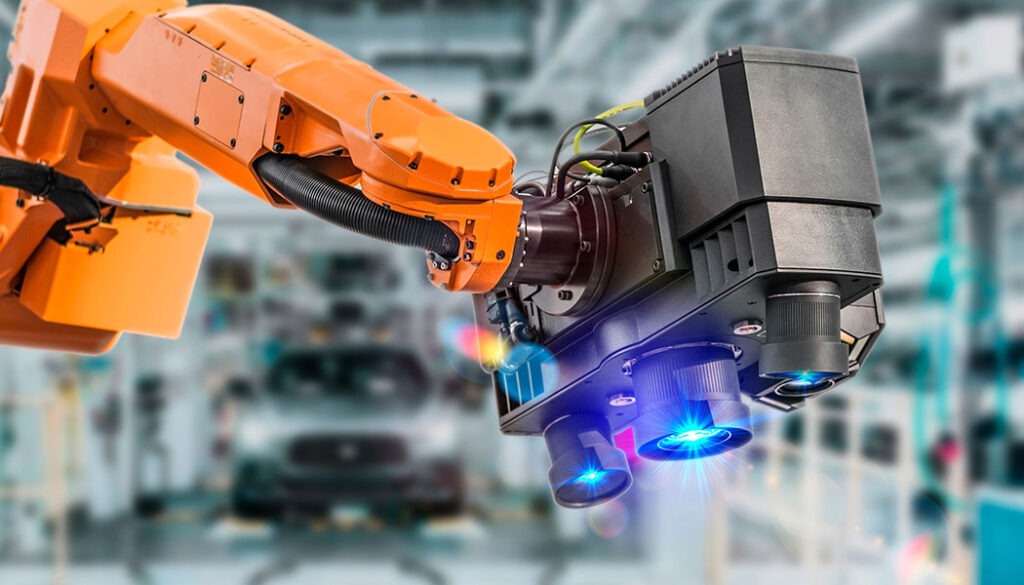
In the industrial world, precision, speed, and reliability are non-negotiable. As factories, warehouses, and production lines become increasingly autonomous, the demand for high-performance imaging solutions has never been greater.
GMSL2 (Gigabit Multimedia Serial Link 2) cameras are playing a pivotal role in scaling industrial automation. They enable real-time, high-resolution vision systems that enhance efficiency, safety, and quality control.
These advanced cameras offer high-speed data transmission, minimal latency, and long-distance connectivity – all critical features for industrial robots, automated inspection systems, and automated guided vehicles.
With seamless integration into AI-driven and edge computing environments, GMSL2 cameras are transforming industrial operations. They are allowing machines to “see” and “react” with unprecedented accuracy.
This article explores how GMSL2 cameras are revolutionizing industrial automation. It explains their key benefits and how emerging technologies further amplify their impact in creating smarter, more autonomous production systems.

What is GMSL2 and Why It Matters
GMSL2 (Gigabit Multimedia Serial Link 2) is a high-speed, low-latency data transmission technology designed to support advanced camera systems in demanding environments. Developed by Maxim Integrated (now part of Analog Devices), GMSL2 enables seamless video and data transfer over long distances with minimal interference, making it an ideal choice for industrial automation.
Also Read: GMSL2 General User Guide
Key Features of GMSL2:
- High-Speed Data Transmission: GMSL2 supports data rates of up to 6 Gbps, ensuring real-time video streaming and rapid sensor feedback for precision-driven industrial applications.
- Long-Distance Connectivity: Unlike traditional camera interfaces, GMSL2 allows transmission distances of up to 15 meters using coaxial cables, making it ideal for large-scale factory setups.
- Superior Resistance to Environmental Noise and EMI: Industrial environments are filled with electromagnetic interference (EMI) from heavy machinery. GMSL2’s robust error correction and signal integrity mechanisms minimize disruptions, ensuring consistent performance in harsh conditions.
Further Reading: GMSL2 Cameras: Definition, Architecture, and Features
How GMSL2 Compares to Other Alternatives
While interfaces like USB, MIPI, and Ethernet offer viable solutions for camera-based applications, GMSL2 often fares better in industrial environments due to the following reasons:
- USB is cost-effective but limited in range and bandwidth, making it unsuitable for high-speed, long-distance imaging.
- MIPI excels in compact, embedded applications but struggles with cable length restrictions and EMI sensitivity.
Ethernet provides longer reach
Applications of GMSL2 Cameras in Industrial Automation
Below are key areas where GMSL2 cameras play a crucial role in enhancing efficiency, precision, and automation in industrial settings.
Quality Control and Inspection Systems
In manufacturing, precision and consistency are critical. GMSL2 cameras enhance quality control by providing high-resolution imaging for real-time defect detection. Unlike conventional inspection methods, these cameras can quickly identify minute imperfections such as surface defects, incorrect alignments, or missing components.
On high-speed production lines, GMSL2 cameras work alongside AI-powered vision systems to assess product quality in milliseconds. The high-bandwidth capabilities ensure that even at high frame rates, images remain sharp and detailed, allowing manufacturers to maintain stringent quality standards without slowing down production. By integrating these cameras with automated sorting and rejection systems, manufacturers can minimize waste and improve efficiency.
Autonomous Industrial Robots
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) and robotic arms rely on vision systems for precise operation in dynamic environments. GMSL2 cameras enable these robots to:
- Navigate with precision by providing real-time imaging for SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) and obstacle detection.
- Recognize and manipulate objects with high accuracy, improving automation in material handling and assembly tasks.
In robotic arms, GMSL2 cameras facilitate real-time object tracking, allowing robots to adapt to variations in shape, size, and position. This is especially useful in assembly lines where components may shift or rotate unpredictably. The low-latency transmission ensures that robotic actions remain synchronized with the camera feed, enhancing accuracy in fast-paced industrial environments.
Smart Warehousing and Logistics

Automated Guided Vehicles
As industries move towards fully automated warehouses, GMSL2 cameras play a pivotal role in streamlining logistics. They are extensively used in:
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): These vehicles use GMSL2 cameras for path planning, collision avoidance, and inventory tracking. The high-speed data transfer enables AGVs to make split-second decisions based on real-time visual inputs.
- Conveyor Belt Monitoring: GMSL2 cameras track products moving along conveyor systems, ensuring smooth operations by detecting bottlenecks or misplaced items. The robust data transmission over long distances helps maintain seamless monitoring across expansive warehouses.
By integrating GMSL2 cameras with warehouse management systems (WMS), businesses can achieve greater efficiency in storage, retrieval, and order fulfillment.
Vision for Predictive Maintenance
Industrial machinery experiences wear and tear over time, leading to unexpected breakdowns and costly downtime. GMSL2 cameras, when combined with vision algorithms, help detect early signs of mechanical failures. These cameras can capture high-resolution images of equipment components, identifying subtle changes that indicate potential issues.
By leveraging AI-powered analytics, manufacturers can process image data to:
- Detect irregularities in motors, belts, and gears.
- Monitor heat signatures for early warning signs of overheating.
- Identify gradual deterioration of machine parts before failures occur.
Predictive maintenance powered by GMSL2 cameras reduces unplanned downtime, extends equipment lifespan, and improves overall operational efficiency.
Edge Computing and AI Applications
With the rise of AI-driven manufacturing, GMSL2 cameras are playing a key role in enabling real-time analytics at the edge. Their high-bandwidth capabilities allow them to feed video data directly into AI/ML models deployed on industrial edge computing platforms such as NVIDIA Jetson and Intel Movidius.
Key applications include:
- Adaptive Manufacturing: AI-powered systems analyze video feeds from GMSL2 cameras to optimize production parameters in real-time. For example, if a deviation in welding patterns is detected, the system can adjust settings automatically to maintain quality.
- Smart Factory Automation: AI-driven vision systems use GMSL2 cameras to monitor processes, detect anomalies, and trigger corrective actions instantly. This results in higher efficiency, reduced waste, and improved production yields.
Benefits of GMSL2 Cameras for Complex Industrial Applications
GMSL2 cameras deliver high-performance, reliable, and scalable imaging solutions, making them essential for precision-driven industrial automation.
High Performance for Demanding Environments
Industrial automation requires cameras that deliver real-time, high-resolution imaging without compromising accuracy. GMSL2 cameras excel in:
- Precision tasks: Their high-speed data transfer (up to 6 Gbps) ensures minimal latency, making them ideal for applications like defect detection, robotic guidance, and predictive maintenance.
- Harsh environments: Unlike traditional cameras, GMSL2 models are designed to operate in high-electromagnetic interference (EMI) settings, such as near heavy machinery or power lines.
- Environmental protection: Many GMSL2 cameras come with IP-rated enclosures, ensuring resistance against dust, water, and fog. This makes them well-suited for outdoor and industrial applications where exposure to contaminants is a concern.
Scalability and Flexibility
GMSL2 technology supports SerDes (Serializer/Deserializer) interfacing, allowing multiple cameras to be connected to a single processing unit. This makes it highly scalable for:
- Large-scale automation: Factories and warehouses with extensive surveillance and inspection needs can efficiently integrate multiple GMSL2 cameras without signal degradation.
- Flexible installation: With cable reach extending up to 15 meters, GMSL2 cameras can be positioned strategically across industrial facilities without requiring complex network infrastructure.
Compatibility with AI and Advanced Automation
As AI-driven automation becomes the industry standard, GMSL2 cameras offer seamless integration with edge computing platforms like NVIDIA Jetson. This allows for:
- Real-time AI-powered analytics: GMSL2 cameras provide high-bandwidth video data, enabling real-time decision-making for tasks like defect detection, robotic movement, and automated sorting.
- Future-proofing: As automation demands grow, industries can scale their AI capabilities without worrying about camera compatibility or data bottlenecks.
Also Read: AI cameras – their significance and applications in embedded vision
Cost Justification
While GMSL2 cameras may have a higher initial cost than alternatives like USB or MIPI cameras, their long-term benefits far outweigh the investment, particularly in mission-critical applications. Key advantages include:
- Lower downtime costs: Reliable, low-latency imaging reduces production halts and maintenance expenses.
- Increased efficiency: Better image quality (compared to USB and MIPI cameras with the same sensor) and real-time processing improve throughput and accuracy, enhancing ROI.
Challenges and Limitations of GMSL2 Cameras
While GMSL2 cameras offer superior performance, their adoption comes with certain challenges.
High Cost
One of the primary concerns is cost. GMSL2 cameras, along with their required SerDes (Serializer/Deserializer) components and specialized infrastructure, are significantly more expensive than alternatives like USB or MIPI cameras. This makes them viable primarily for high-performance applications where the benefits justify the investment.
Integration Issues
Integration complexity is another hurdle. Unlike plug-and-play solutions, GMSL2 cameras require careful system design, including dedicated cables, connectors, and power delivery systems. Engineers must ensure compatibility with host processors, frame grabbers, and middleware, increasing development time and costs.
Specialized Requirements
Additionally, GMSL2 technology demands specialized cabling to maintain signal integrity over long distances. The use of coaxial cables and Power over Coax (PoC) simplifies wiring but requires precise implementation to avoid signal degradation.
Limited Suitability
Finally, GMSL2 cameras are best suited for applications demanding extreme reliability, high-speed data transfer, and low-latency imaging. For less demanding industrial tasks, lower-cost options may be more practical, limiting GMSL2’s widespread use.
Despite these challenges, industries requiring cutting-edge imaging and automation continue to adopt GMSL2 for its unmatched capabilities in high-stakes environments.
Future Trends and Innovations in GMSL2 Camera Technology
GMSL2 camera technology is continuously evolving to meet the growing demands of industrial automation.
One major area of advancement is high dynamic range (HDR) imaging, which enhances visual clarity in challenging lighting conditions. Though HDR cameras have been around for a while, newer developments are helping improve overall image quality. This development, however, is not limited to GMSL2 cameras but also applies to other types of cameras.
Additionally, multi-camera synchronization is improving, allowing for precise coordination between multiple vision systems in industrial settings. Innovations in noise resistance and bandwidth expansion are also pushing GMSL2 performance further, enabling more detailed and real-time imaging even in high-interference environments.
As smart factories and IoT-driven automation gain momentum, GMSL2 cameras are becoming a critical part of these ecosystems. Their ability to provide high-speed, low-latency imaging supports applications such as predictive maintenance, robotic guidance, and real-time quality control.
Another key trend is the integration of AI-powered software with GMSL2 cameras. By combining machine learning algorithms with high-bandwidth video streams, manufacturers can enable adaptive manufacturing processes, where production lines self-optimize based on real-time data.
Beyond manufacturing, GMSL2 is expanding into new frontiers like autonomous heavy machinery, mining vehicles, and complex industrial inspection systems. Companies are already deploying these solutions, and adoption is expected to rise as industries seek more reliable and intelligent vision systems to drive automation at scale.
Wrapping Up
GMSL2 cameras play a pivotal role in advancing industrial automation by delivering high-speed, high-resolution imaging with minimal latency. Their ability to withstand harsh environments, integrate seamlessly with AI and edge computing systems, and support large-scale automation makes them a valuable investment for high-stakes applications.
As industries continue to embrace smarter, data-driven operations, TechNexion’s GMSL2 camera systems offer the ideal solution for next-generation automation projects that demand cutting-edge vision technology. For more information or personalized support, feel free to get in touch with our experts.
Related Products
Get a Quote
Fill out the details below and one of our representatives will contact you shortly.