Imagine an autonomous robot navigating a busy warehouse, dodging workers and forklifts in real time. Or a smart surveillance system that instantly identifies security threats without relying on a distant cloud server. In both cases, AI needs to process visual data fast. Right where the data is collected.
This is the power of edge AI vision, where machines analyze high-speed imagery locally to make split-second decisions. But here’s the catch! Traditional camera interfaces often struggle with bandwidth, latency, and complex wiring, creating bottlenecks for AI performance.
Enter GMSL2 cameras, the unsung heroes of AI vision. These high-speed cameras revolutionize edge computing by delivering ultra-low latency, high-resolution video over long distances, all through a single coaxial cable. Whether in robotics, autonomous vehicles, or industrial automation, GMSL2 ensures that AI sees the world clearly and reacts instantly.
In this guide, we’ll break down how GMSL2 cameras supercharge edge AI and why they’re becoming essential for next-gen vision systems.

Understanding GMSL2 Cameras
GMSL2 (Gigabit Multimedia Serial Link 2) is a high-speed camera interface developed by Maxim Integrated (now part of Analog Devices) to solve a critical problem in AI vision: the need for high-bandwidth, low-latency video transmission over long distances.
Originally designed for automotive applications, GMSL technology has evolved into its second generation (GMSL2), offering higher data rates, improved signal integrity, and better electromagnetic interference (EMI) resistance, features essential for AI-driven vision systems.
Further Reading: GMSL2 Cameras: Definition, Architecture, and Features
How GMSL2 Outperforms Traditional Camera Interfaces
Unlike interfaces like MIPI CSI or USB, which suffer from limited cable reach, GMSL2 transmits up to 6 Gbps per lane over coaxial or shielded twisted-pair (STP) cables, maintaining image quality across distances upto 15 meters. It also supports Power-over-Coax (PoC), eliminating the need for separate power lines. These advantages reduce complexity, making GMSL2 ideal for real-time, high-speed AI vision.
Why Industries Are Shifting to GMSL2
From autonomous vehicles to factory automation and AI-powered surveillance, industries demand faster, more reliable vision systems. GMSL2’s ability to handle multi-camera synchronization, low latency, and high-resolution streaming makes it the preferred choice for AI-driven applications where every millisecond counts.
The Need for Edge AI in Vision Applications
AI is only as good as the data it processes. And in high-speed vision applications, delays can mean the difference between success and failure. Whether it’s an autonomous vehicle avoiding an obstacle or a factory robot detecting a defective product, real-time AI vision requires instant decision-making. That’s why AI is shifting away from centralized cloud processing and moving closer to the data source. A shift known as Edge AI.
Why AI Needs to Move Closer to the Data Source
Traditional AI vision systems rely on cloud computing to process images and video streams. While the cloud offers immense processing power, it introduces latency, bandwidth constraints, and security risks. When AI must react in milliseconds, sending data to a remote server isn’t practical. Edge AI eliminates this bottleneck by processing data locally, ensuring faster, more efficient, and more reliable AI-powered vision.

Edge AI vs. Cloud AI: Key Trade-Offs
- Latency: Cloud AI introduces delays due to network communication, while Edge AI enables near-instant processing.
- Bandwidth: Streaming high-resolution video to the cloud consumes excessive bandwidth. Edge AI processes data locally, reducing transmission needs.
- Security & Privacy: Sensitive video feeds stored in the cloud are vulnerable to breaches. Edge AI keeps data on-premise, enhancing security.
- Scalability: Cloud AI can handle complex workloads but may struggle with real-time demands. Edge AI optimizes for speed and efficiency.
Where Real-Time Vision Processing is Critical
- Autonomous Vehicles: AI must instantly recognize objects, pedestrians, and road signs to prevent accidents.
- Smart Manufacturing: High-speed cameras detect defects in milliseconds, improving quality control.
- Surveillance & Security: AI-powered vision systems analyze live video feeds for threats without delays.
- Medical Imaging: Robotic-assisted surgeries rely on real-time AI analysis for precision procedures.

How GMSL2 Cameras Improve Edge AI Performance
GMSL2 ensures fast, reliable, and high-fidelity visual data. Here’s how it enhances AI performance at the edge.
High-Speed, Low-Latency Imaging
AI-powered vision systems need to see and react instantly. Traditional camera interfaces often introduce delays due to limited bandwidth, slow data transfer, or buffering issues. But GMSL2 eliminates these roadblocks. By offering up to 6 Gbps per lane, GMSL2 cameras ensure that high-resolution video streams reach AI processors without lag. This ultra-fast data transmission enables AI models to process images in real time, which is crucial for applications like autonomous driving, industrial inspection, and surveillance.
Enhanced Synchronization for Multi-Camera Setups
Many AI applications, such as robotics, ADAS (Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems), and smart manufacturing, require multiple cameras working together. However, synchronizing video feeds across different cameras is a challenge with traditional interfaces, often leading to misaligned data and inaccurate AI predictions. GMSL2 solves this problem by facilitating precise frame synchronization, ensuring that multiple cameras capture images at the exact same moment. This is particularly beneficial for:
- 3D Vision & Depth Perception: Multi-camera setups use GMSL2’s synchronized feeds to create accurate stereo vision for AI-powered depth estimation.
- Object Tracking & Motion Analysis: AI models can track moving objects more accurately, as all cameras are perfectly aligned in time.
Minimized Data Loss and Compression Artifacts
Image quality is critical for AI vision systems. Many traditional camera interfaces rely on lossy compression to reduce data size, which can introduce artifacts, noise, and loss of detail, leading to inaccurate AI decisions. GMSL2 preserves image integrity through:
- Lossless Transmission: Unlike other interfaces that compress video feeds, GMSL2 ensures full-fidelity data transfer over long distances.
- Error Correction Mechanisms: Built-in error detection and correction maintain signal quality, even in high-interference environments.
- Improved AI Accuracy: High-quality image inputs lead to better object detection, classification, and tracking performance.
Power Efficiency & Bandwidth Optimization
Edge AI devices must balance performance with power efficiency, especially in battery-powered applications like drones, robots, and mobile medical devices. GMSL2 optimizes both by:
- Power-over-Coax (PoC) Technology: Delivering power and data through a single cable, reducing wiring complexity and power consumption.
- High Bandwidth, Low Overhead: Transmitting more data with fewer cables, maximizing efficiency in embedded AI systems.
- Reduced Processing Load: Less data loss and compression artifacts mean AI processors spend less time correcting errors, improving efficiency.
What’s Limiting Edge AI and GMSL2 Today?
As AI vision systems become more complex and widespread, several bottlenecks still hinder the full-scale adoption of GMSL2-based edge AI. Let’s break them down.
Hardware Constraints
AI workloads are notoriously compute-intensive, and processing high-resolution video streams in real time requires powerful edge processors. While GPUs, NPUs (Neural Processing Units), and dedicated AI accelerators have made significant strides, many edge devices, such as embedded systems and IoT devices, lack the raw computing power needed for advanced AI tasks.
The result?
Bottlenecks in inference speed, increased latency, and higher power consumption. To fully utilize GMSL2 cameras, edge hardware must evolve to handle multi-stream AI processing more efficiently.
Scalability Issues
GMSL2 excels in high-performance, low-latency applications, but scaling it across large AI vision networks presents logistical and cost challenges.
- Infrastructure Overhead: Large-scale deployments require multiple cameras, high-speed data links, and advanced processing units, driving up costs.
- Complex Integration: GMSL2 cameras demand dedicated deserializers and specialized hardware, making integration more complex than standard camera interfaces.
- Wiring & Deployment: While Power-over-Coax (PoC) simplifies wiring, deploying and maintaining large-scale GMSL2 camera networks can still be challenging.
Until cost-effective, plug-and-play solutions emerge, scalability remains a hurdle for industries looking to adopt GMSL2 on a massive scale.
Data Management & Storage
The sheer volume of data generated by GMSL2 cameras presents challenges in storage, bandwidth, and processing efficiency.
- High-Resolution Overhead: 4K+ video streams generate massive amounts of data, putting pressure on storage systems.
- Efficient Compression Needed: Lossless data transfer is great for AI, but without efficient compression, storage demands quickly escalate.
- Real-Time Processing Bottlenecks: AI systems must analyze large video streams on the fly, requiring fast memory, optimized algorithms, and edge computing enhancements.
Standardization & Compatibility
Unlike traditional camera interfaces (USB, MIPI, GigE Vision), GMSL2 lacks a universally accepted standard for AI vision applications.
- Proprietary Implementations: Different vendors use custom GMSL2 implementations, leading to compatibility issues.
- Software & API Fragmentation: Developers face challenges in integrating GMSL2 cameras with AI frameworks due to inconsistent driver support.
- Industry Adoption Lag: Many industries still hesitate to switch due to the lack of standardized tools, APIs, and cross-platform support.
The Hidden Costs of High-Speed AI Vision
From power consumption to data security concerns, here are the hidden challenges that come with high-speed AI vision.
Energy Consumption
Real-time AI processing demands significant computational power, and GMSL2-equipped systems are no exception. High-resolution video streams require power-hungry AI accelerators, GPUs, and FPGAs, which can strain battery-operated and embedded devices. Efficient power management strategies, such as dynamic voltage scaling and optimized AI models, are essential to keep energy demands in check.
Infrastructure Costs
Deploying GMSL2-based AI vision systems isn’t just about adding cameras; it requires specialized deserializers, high-speed networking, and advanced processors capable of handling vast data loads. This infrastructure comes with higher initial costs and integration complexity, making it a significant investment for businesses and industries scaling AI vision applications.
Maintenance & Longevity
Unlike traditional cameras, GMSL2-based systems rely on high-bandwidth connections and specialized components that require regular maintenance. Over time, connector wear, cable degradation, and processing unit upgrades become critical factors in keeping these systems functional and cost-effective for long-term use.
Data Privacy & Security Risks
Though processing happens on the edge, with vast amounts of real-time visual data being analyzed, security is still a major concern. Unauthorized access, hacking risks, and regulatory compliance pose challenges for industries handling sensitive information. Implementing robust encryption, secure boot mechanisms, and AI-driven anomaly detection is essential to protect AI vision systems from cyber threats while ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
Wrapping Up
GMSL2 cameras are redefining AI-driven vision, bringing high-speed, low-latency imaging to the edge like never before. Their ability to deliver synchronized, high-fidelity data in real time is pushing the boundaries of what AI can achieve in autonomous systems, industrial automation, and beyond. As edge computing evolves, the synergy between AI and GMSL2 technology will be instrumental in unlocking faster, smarter, and more efficient vision applications.
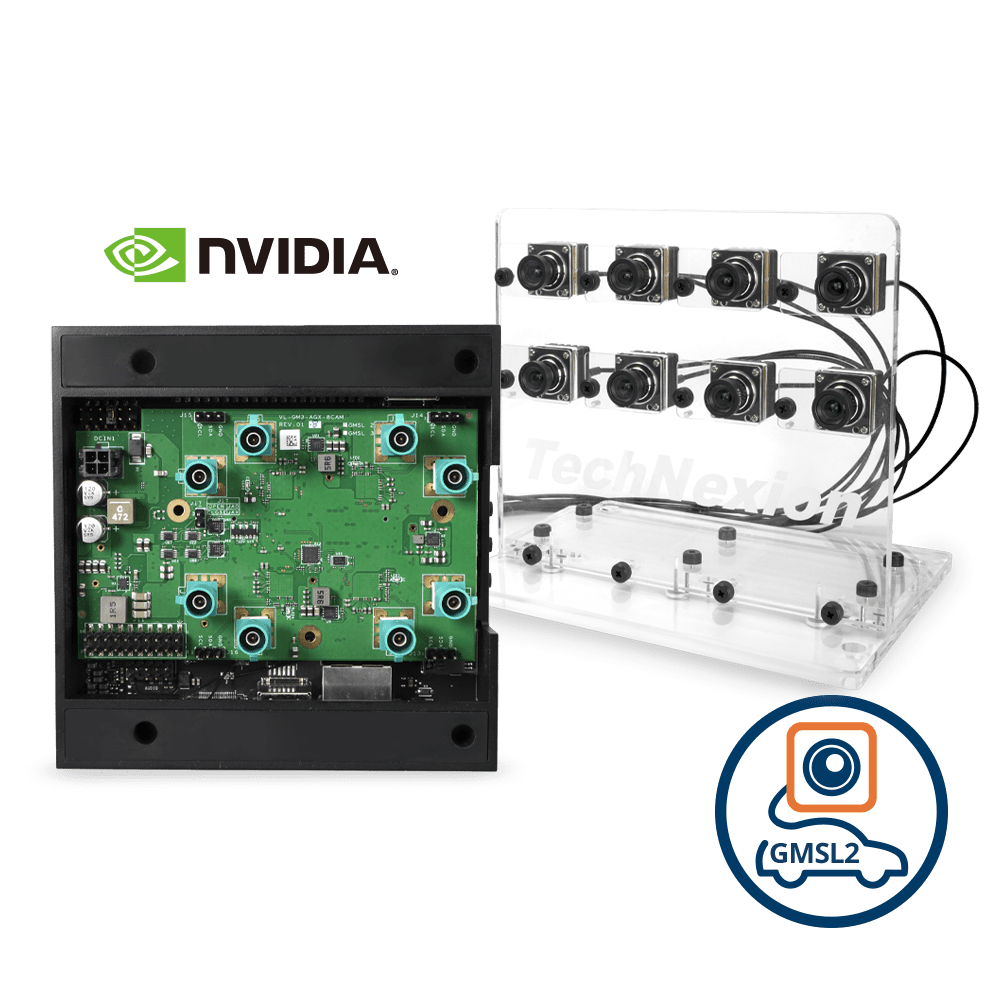
TechNexion drives edge AI innovation with GMSL2 cameras and embedded computing solutions. Designed for real-time AI processing, these cameras offer low-latency, synchronized imaging for robotics, automation, and autonomous vehicles. Combined with AI-ready SoMs and industrial carrier boards, they enable seamless AI integration at the edge.
To learn more about our product portfolio and solutioning approach, feel free to contact us.
Related Products
Get a Quote
Fill out the details below and one of our representatives will contact you shortly.