Embedded vision is revolutionizing the industrial sector by automating a wide array of tasks – from inspection and navigation to material handling. For instance, automated inspection camera systems powered by embedded vision can swiftly identify product defects on production lines. This ensures higher quality standards without human intervention.
Similarly, autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) equipped with vision systems can efficiently navigate complex warehouse environments, optimizing material flow and reducing labor costs. These advancements are not just limited to existing applications. Embedded vision is paving the way for smarter manufacturing and industrial automation by integrating vision capabilities into newer, innovative applications.
This blog post delves into the various trends and technologies in embedded vision that are reshaping industrial automation.
What Is Embedded Vision?
Embedded vision refers to the integration of visual processing capabilities into machines and devices, enabling them to interpret and act on visual data. Unlike machine vision systems, which rely on external computers for processing, embedded vision systems have built-in processors that handle image capture and analysis in real time.
For example, in a packaging plant, an embedded vision system can be used to inspect products on a conveyor belt. The system captures images of each product as it passes by and analyzes them for defects like incorrect labeling or damaged packaging. If a defect is detected, the system can trigger a rejection mechanism. This can help remove the faulty product from the line. This ensures only high-quality items reach the end customer.
This integration of vision technology into machinery enhances efficiency, reduces the need for human intervention, and improves accuracy. Embedded vision is crucial for advancing automation, making industrial processes smarter and more responsive to real-time data.
Further reading: Embedded Vision vs. Machine Vision – Everything You Need to Know
The Evolution of Embedded Vision
Embedded vision has come a long way since its inception. Here is a look at each major stage in its advancement.
The Early Days
Initially, embedded vision systems were limited by the computational capabilities of early embedded processors. These systems could perform basic image processing tasks. However, they struggled with complex analyses and real-time processing.
Processing Power
The turning point came with the development of more powerful and energy-efficient processors, like the NVIDIA Jetson, specifically designed for embedded applications. This leap allowed for the implementation of advanced image processing techniques directly on the devices. This, in turn, eliminated the need for external computing resources and the dependency on the cloud.
Sensor Technology Advancements
Advancements in sensor technology also played a crucial role. High-resolution and multispectral sensors provided more detailed and diverse data. This enabled embedded vision systems to perform tasks that were previously impossible. For instance, in agricultural automation, embedded vision systems can now assess crop health by analyzing images across different spectral bands, including near-infrared regions.
Integration of AI
The integration of machine learning and AI has further propelled the evolution of embedded vision. These technologies enable systems to learn from data, improving their accuracy and adaptability over time. Today, embedded vision systems are capable of real-time decision-making. This makes them indispensable in various industrial applications, from quality control to autonomous navigation.
Embedded Vision Trends in the Industrial Sector
Innovations in embedded vision technology are enabling new applications and enhancing existing processes. Let’s delve into the key embedded vision trends that are transforming the industrial sector.
The Integration of AI and Embedded Cameras
As stated earlier, AI is revolutionizing embedded vision systems to a great extent. This, in turn, is reshaping the way industries operate. With AI, embedded vision systems can perform complex tasks such as intelligent product sorting, quality control, and predictive maintenance.
For example, in a manufacturing plant, AI-powered embedded cameras can identify and categorize products based on visual attributes like shape, size, and color. This leads to faster, more accurate sorting processes, reducing errors and increasing efficiency.
AI also enhances defect detection. Traditional systems often miss subtle flaws, but AI algorithms can learn from data and improve over time. This results in higher quality products and reduced waste. In addition, AI enables real-time decision-making, allowing systems to adapt to changing conditions on the fly.

Conveyor belt in a manufacturing plant
Furthermore, AI-driven embedded vision systems can conduct predictive maintenance by analyzing equipment conditions and performance. By identifying potential issues before they cause failures, these systems help prevent costly downtime and extend machinery lifespan. This leads to more efficient industrial operations.
Rise of RGB-IR Cameras
RGB-IR cameras are gaining popularity in industrial settings, particularly for surveillance in warehouses and factories. These cameras capture both visible light (RGB) and infrared (IR) light, all in a single camera module, without the need for external IR-cut filters.
During the day, the RGB pixels of the sensor capture detailed color images. At night, the IR pixels of the sensor offer clear visibility even in low-light conditions. With RGB and IR data captured using the same sensor, both are separated during the processing stage to obtain the best output. This dual functionality ensures continuous monitoring and security, crucial for protecting valuable assets and maintaining safety standards.
For instance, in a surveillance system used in warehouses, RGB-IR cameras can monitor the premises under visible light during the day and detect intrusions or equipment malfunctions at night under an IR light source. This 24/7 surveillance capability enhances operational efficiency and security.
Additionally, RGB-IR cameras are being used for environmental monitoring within industrial settings. They can detect temperature variations and gas emissions invisible to the naked eye, ensuring safe working conditions and helping comply with environmental regulations.
Also read: NIR Cameras in Embedded Vision – Advantages and Applications
Increase in Use of RGBD Cameras
RGBD cameras, which capture color (RGB) and depth (D) information, are becoming essential in industrial automation. These cameras provide a three-dimensional view of the environment, enabling precise navigation and interaction.
In robotics, RGBD cameras allow robots to understand and navigate complex environments. Autonomous robots use these cameras to avoid obstacles, pick and place objects, and perform tasks with high precision. The biggest advantage is that measuring depth as well as capturing images can be done using a single camera system.
For example, in warehouses, autonomous robots equipped with RGBD cameras can create 3D maps of the interiors while taking stock of the inventory on the shelves.
RGBD cameras are also instrumental in quality control. They enable detailed inspection by providing both visual and spatial data. For example, in electronics manufacturing, these cameras can inspect solder joints and components on printed circuit boards (PCBs) more effectively. While the 2D camera detects the defects, the 3D camera can measure the depth of a dent or any other deformations on the surface of the objects.
Connected Systems
The integration of IoT sensors, LiDAR, and embedded cameras is creating highly connected industrial systems. These technologies work together to enhance the effectiveness of industrial processes.
Embedded cameras provide a surround view, capturing comprehensive visual data. LiDAR measures depth, offering detailed spatial information. IoT sensors track motion, speed, temperature, and other parameters. Together, these technologies enable advanced applications like autonomous navigation and machine tending.
For instance, in autonomous vehicles used in factories, embedded cameras and LiDAR provide a detailed view of the surroundings. IoT sensors monitor vehicle performance, ensuring optimal operation. This integration improves efficiency, safety, and accuracy in tasks like picking and placing items or transporting materials.
Furthermore, the data collected by these interconnected systems can be analyzed using big data analytics software to optimize production processes. With this, companies can streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance productivity.
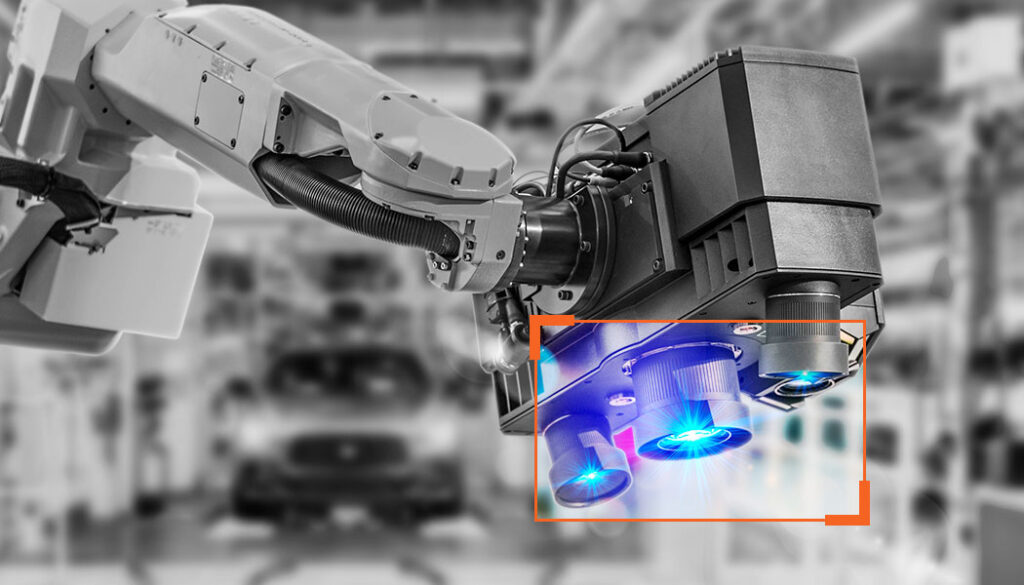
Camera-enabled robotic arms
Miniaturization and Bulking of Cameras
In embedded vision, there is a simultaneous trend towards miniaturization and the use of larger sensor cameras. Advances in camera technology are enabling the development of smaller, more powerful cameras that can be integrated into compact and tight spaces. Mini drones, industrial tablets, and wearable devices are examples.
At the same time, many industrial applications demand larger sensor cameras for their superior sensitivity and broader coverage. Generally, cameras with sensors larger than 1/2.2 inch are considered “large” in this context. These cameras have larger pixel sizes, providing higher sensitivity, better low-light performance, and a larger field of view in applications such as smart surveillance, robotics arms, and quality inspection systems.
This dual trend ensures that embedded vision systems can meet diverse application needs. It helps balance the benefits of compact design with the advantages of enhanced imaging capabilities.
Enhanced Connectivity with 5G Technology
The advent of 5G technology is significantly enhancing the connectivity of embedded vision systems in industrial settings. 5G offers faster data transfer rates, lower latency, and improved reliability compared to previous wireless technologies. This high-speed connectivity is particularly beneficial for applications such as remote monitoring.
Additionally, 5G connectivity supports the integration of more devices and sensors, creating a highly interconnected and responsive industrial ecosystem. This allows for better coordination and synchronization of various processes, further enhancing operational efficiency.
Enhanced Cybersecurity Measures
As embedded vision systems become more integral to industrial automation, the need for robust cybersecurity measures is increasing. These systems often handle sensitive data and control critical processes, making them potential targets for cyber-attacks.
Advanced cybersecurity protocols are being integrated into embedded vision systems to address these challenges. This includes encryption of data streams, secure boot processes, and real-time monitoring for potential threats. For instance, in a smart factory, encrypted communication between embedded cameras and control systems can prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
Moreover, incorporating AI into cybersecurity can provide an additional layer of protection. AI can continuously analyze network traffic and detect anomalies that may indicate a cyber-attack, allowing for proactive and swift responses to potential threats.
TechNexion – Redefining How Vision Impacts Industrial Automation
TechNexion offers a comprehensive range of camera solutions designed for industrial applications, redefining how vision technology enhances automation processes. Our cameras boast high-resolution sensors that capture detailed and precise images, essential for tasks such as quality control and defect detection.
Our global shutter cameras eliminate rolling shutter artifacts, making them ideal for high-speed operations and ensuring accurate imaging of fast-moving objects. Our cameras comes with an optional IP-rated enclosure, providing robust protection against dust, water, and other environmental factors. This durability ensures reliable performance even in the most demanding industrial settings.
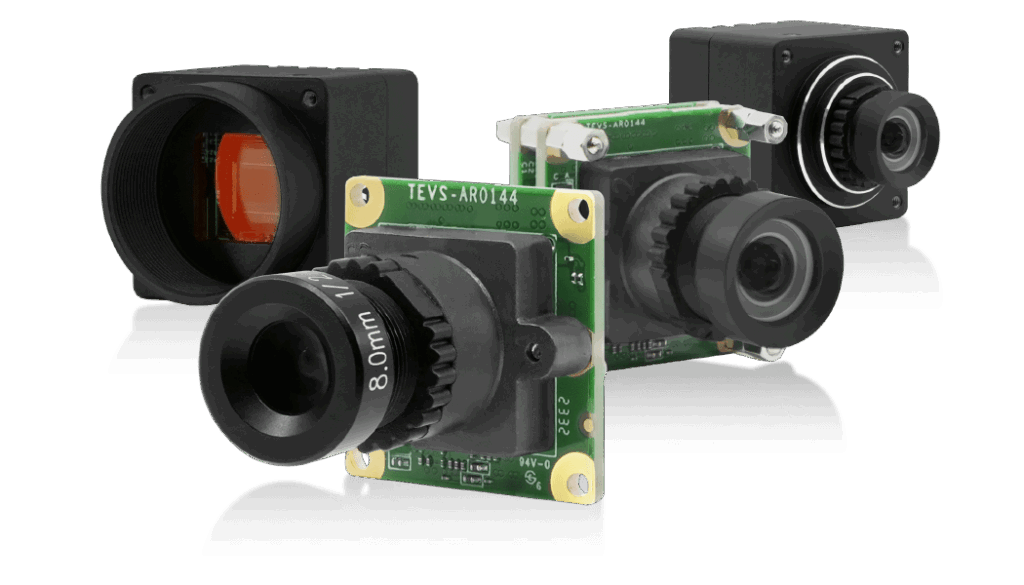
TechNexion’s Embedded Cameras
Whether it’s for continuous surveillance in factories and warehouses, detailed inspection on assembly lines, or enabling autonomous navigation in industrial robots, TechNexion’s cutting-edge camera solutions are pivotal in advancing industrial automation, ensuring efficiency, accuracy, and operational excellence.
Get in touch with us today to explore how TechNexion’s advanced camera solutions can elevate your industrial automation processes.
Related Products
Get a Quote
Fill out the details below and one of our representatives will contact you shortly.