Have you ever wondered how machines can “see”? The answer lies in the technologies of embedded vision and machine vision. There is often confusion between the two terms. And in fact, there is a thin line between the two.
But what exactly are these two technologies, and how do they differ? While embedded vision and machine vision are both used for image capture, processing, and analysis, their applications and capabilities differ. Machine vision systems are used in applications that require extensive data processing and make use of external PCs or the cloud to run image processing tasks. Embedded vision systems are used in vision applications that are less data-hungry and do not require heavy processing, as the vision processing function is typically connected directly to the camera sensor.
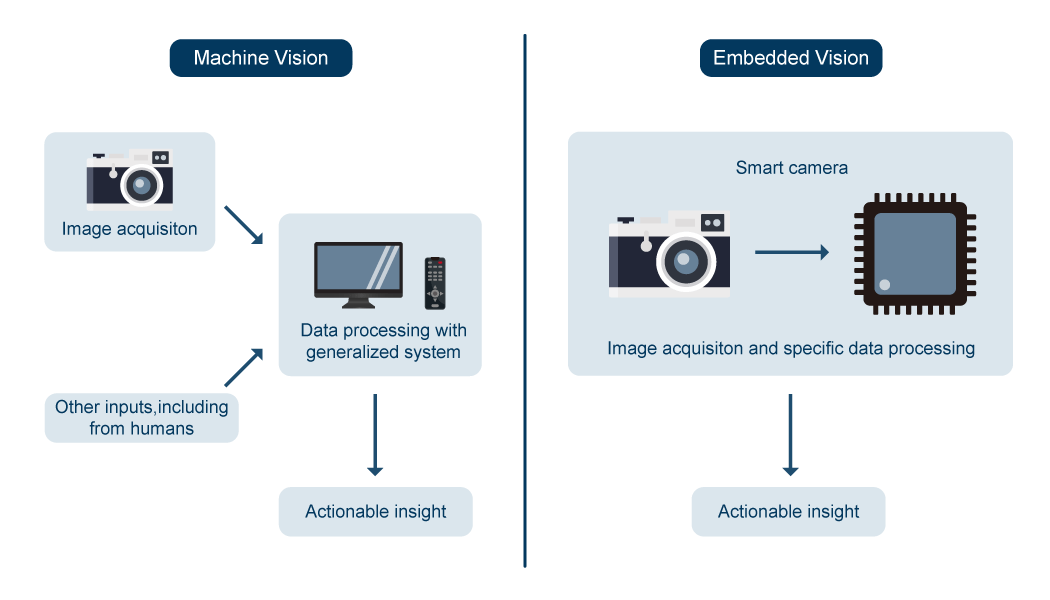
Advancements in camera and processing technologies have enabled embedded vision systems to catch up and become almost as powerful as machine vision systems.
Image here. Showing a block diagram of a Machine Vision System and an Embedded Vision system. In the Machine Vision system, the block is a remotely located computer or server connected to a camera. In an embedded vision system, the camera sensor and the vision processor are located in the same box.
In fact, many today lean toward embedded vision because of its affordability, compactness, and the convenience of executing image processing on-device or on-board.In this article, we will explore both technologies’ similarities, differences, and applications.
What is Machine Vision?
Machine vision enables computers or machines to “see” and interpret visual information. It involves using cameras, image processing software, and hardware components to capture, analyze, and make decisions based on visual data.
Machine vision systems often utilize industrial or commercial PCs to handle the computational workload involved with the processing of image data. These robust PCs are equipped with specialized hardware and software that enable efficient image analysis and provide the necessary computing power for complex machine vision tasks. Typically, a machine vision system includes:
- Cameras: These are mostly specialized industrial cameras designed for specific applications. These cameras capture images or video footage that are then processed by the host system.
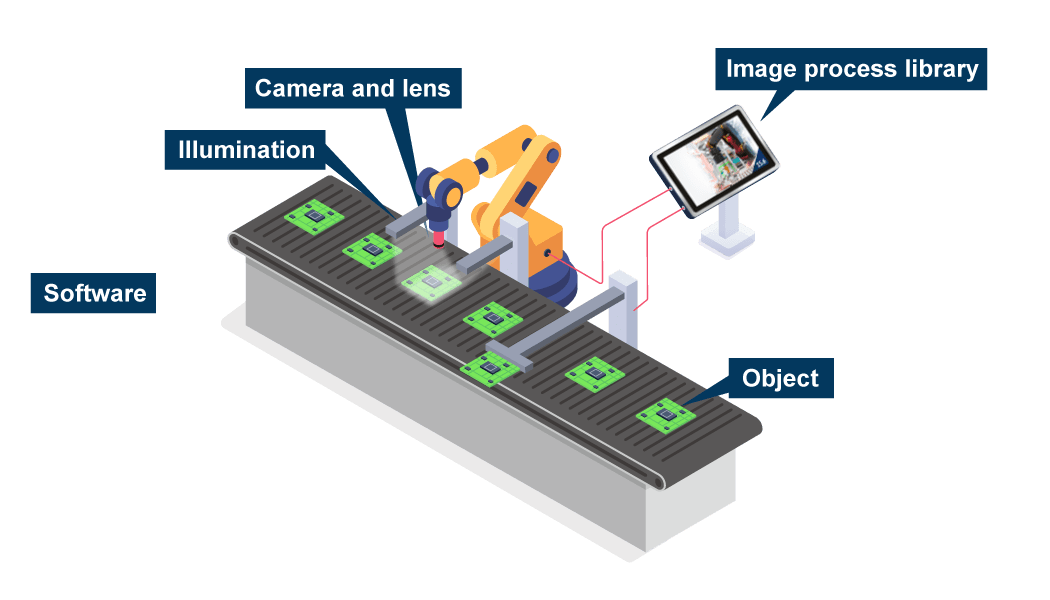
Components of a machine vision system
- Image Processing Software: While some machine vision cameras are plug-and-play, a few others might need software applications specifically designed for image analysis and processing. These software programs use AI/ML based computer vision algorithms to analyze and extract relevant information from images for purposes such as object recognition, measurement, or defect detection.
- Lighting and Optics: Proper lighting and optics play a crucial role in machine vision systems to ensure high-quality image capture. Various types of lighting techniques, such as LED lighting or infrared illumination, are used to optimize image visibility and contrast.
- Hardware Components: Machine vision systems may include additional hardware components like frame grabbers, interface cards, or specialized processors to facilitate data transfer and accelerate image processing tasks.
Machine vision is used in a wide range of industries for applications such as quality control in manufacturing, object recognition and sorting, robotics and automation, and surveillance and security.
What is Embedded Vision?
In the case of embedded vision, processing capabilities are integrated directly into the vision device. This allows them to “see” and interpret visual data on-device and on-board, and provide useful insights. This offers several advantages: compactness, lower cost of operations, and real-time responsiveness.
Embedded vision systems are commonly found in devices such as drones, autonomous vehicles, smart traffic devices, and other innovative Internet of Things (IoT) devices. They enable autonomous decision-making based on visual information by integrating vision processing capabilities into these devices. This is made possible by integrating embedded cameras with processors such as TI Jacinto TDA4VM, NVIDIA Jetson Orin, NXP i.MX8, etc.
The ability to process data on-device or on-board makes embedded vision systems more compact and easier to use once integrated, providing greater flexibility and efficiency in various applications.
Embedded Vision vs. Machine Vision
Though both embedded vision and machine vision help machines see, the two have key differences.
| Parameters | Machine Vision | Embedded Vision |
|---|---|---|
| Image processing | Image processing is performed using a separate PC connected to the machine vision camera. | Image processing is carried out on-device using dedicated processors such as NVIDIA Jetson, TI Jacinto, NXP, etc. |
| Image analysis | PC-based image analysis, in some cases, data is sent from the PC to cloud-based software for detailed analysis using computer vision algorithms. | Embedded vision systems primarily perform analysis on the device itself using edge computing, utilizing AI/ML/computer vision algorithms. Data may be uploaded to the cloud for heavy analyses if the on-device processor cannot handle it. |
| Size | Machine vision systems are bulkier as they consist of a camera system and a separate PC, often industrial or commercial in size. | Embedded vision systems are more compact as the processing takes place on-device. The size of processors continues to decrease with advancements in technology, although certain compact processor families like NXP i.MX may have limited AI performance. |
| Cost | Machine vision cameras can be expensive to operate due to multiple components like the camera, PC, and possible software subscriptions for cloud-based analysis. | Embedded vision systems are generally more cost-effective in the long run as they reduce ongoing operational costs. However, initial capital expenditure (capex) may be higher for embedded vision depending on the camera type and processor used. |
| Ease of integration | Machine vision systems are generally easier to integrate as they use standard interfaces and can be directly connected to a PC for immediate operation. Some engineering expertise may still be required. | Embedded vision systems require some engineering expertise for integration, which may vary based on the complexity of the application and components used. Assistance from camera experts like TechNexion may be necessary for camera integration. |
| Speed of decision-making | To achieve near real-time decision-making, machine vision systems require fast hardware and software for efficient data transfer and analysis. | Embedded vision systems excel in real-time decision-making as processing occurs on-device without the need for specialized setups to transfer data quickly to the cloud for analysis. |
| Flexibility | Machine vision systems tend to be general purpose. Through configuration and software, a machine vision system can be used for different tasks. | Embedded vision systems tend to be designed for a specific task. Optics, sensor, processor, and software analytics are all chosen, tuned, and cost optimized for a specific use-case. |
Applications of Machine Vision
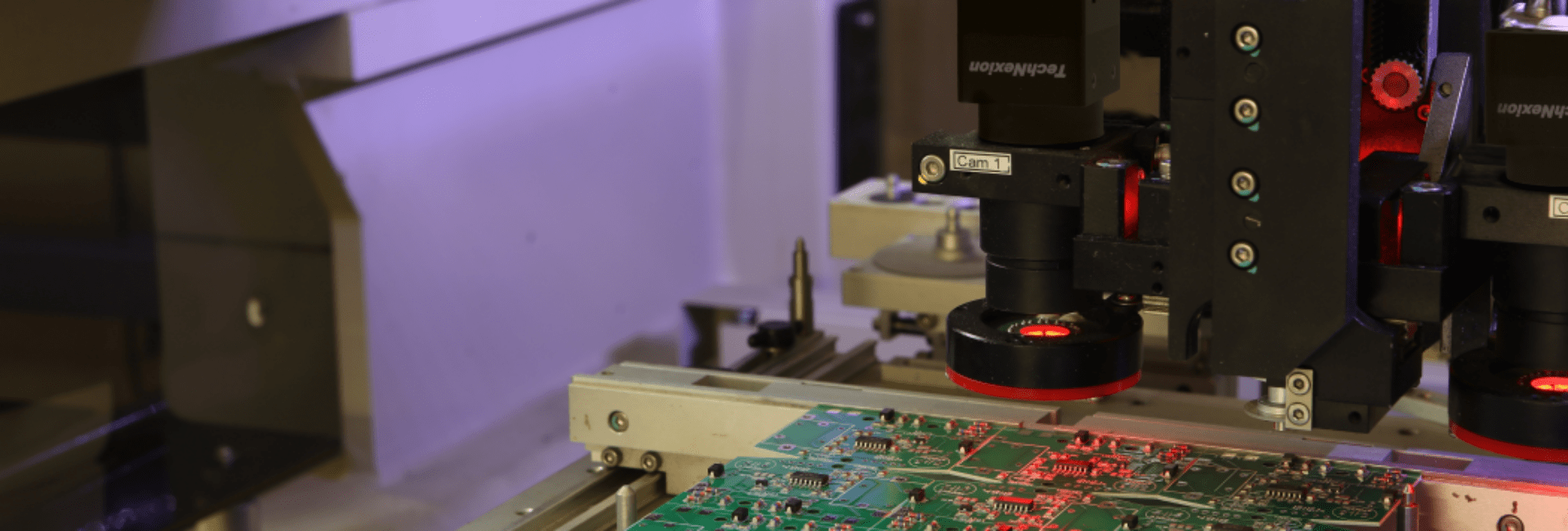
With the wide adoption of machine vision, the manufacturing industry has seen a transformation notably in the areas of quality control and factory automation.
Here are several popular use cases of machine vision:
Quality Inspection
Machine vision systems are extensively used to inspect and assess the quality of products during the manufacturing process. These systems can detect defects, such as surface imperfections, incorrect dimensions, and misalignments. By automatically identifying and rejecting defective products, machine vision ensures that only high-quality items reach the market, improving overall product quality and customer satisfaction.
Assembly Verification
Machine vision is employed to verify the correct assembly of components in manufacturing processes. By analyzing images and comparing them with predefined templates or specifications, machine vision systems can determine if all the necessary components have been correctly positioned and assembled. This ensures that products meet the required standards and eliminates the risk of faulty assemblies.
Measurement and Metrology
Machine vision systems enable accurate and precise measurements of products and components. They can measure dimensions, angles, and tolerances with high accuracy, ensuring compliance with specifications. This is particularly useful in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics, where precise measurements are crucial for product performance and safety.
Robotics and Automation
Machine vision plays a vital role in enabling robotics and automation in manufacturing. By providing visual perception capabilities, machine vision systems guide robots in tasks such as pick-and-place operations, part recognition, and assembly. This enhances production efficiency, increases productivity, and reduces human intervention in repetitive or hazardous tasks.
China, with its extensive manufacturing capabilities, has emerged as one of the largest markets for machine vision technology. Many modern factories in China employ machine vision systems to optimize production processes, enhance quality control, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Applications of Embedded Vision
Embedded vision has been limited to low-end camera applications due to constraints in processing abilities.
With the more advanced processors available now, data-hungry applications like robotics can now use embedded vision to enable navigation, obstacle detection, and object recognition.
Here are some notable applications of embedded vision:

Smart Traffic Management
Embedded cameras can be integrated into traffic management systems to monitor and analyze traffic conditions in real time. They enable license plate recognition, traffic flow analysis, and incident detection. This helps optimize traffic flow, improve road safety, and enhance overall transportation efficiency.
Robotics
Embedded vision plays a crucial role in enabling various robotic applications. Robots equipped with embedded vision can navigate their environment, detect obstacles, and recognize objects for manipulation and interaction. This technology is utilized in robotic arms, pick-and-place robots, autonomous vehicles, and other robotic systems across industries.
Precision Agriculture and Vertical Farming
Embedded vision is employed in agricultural applications to optimize farming processes. It enables automated weed detection and removal, precise planting, crop monitoring, and harvesting. In vertical farming, embedded vision systems assist in maintaining optimal growing conditions and monitoring plant health, leading to increased productivity and resource efficiency.
Smart City Solutions
Embedded vision contributes to the development of smart city infrastructure. It is used in smart traffic management systems, intelligent street lighting solutions, and surveillance systems for public safety and security. Embedded vision helps in monitoring traffic patterns, managing energy consumption, and enhancing surveillance capabilities.
Healthcare and Life Sciences
Embedded vision technology finds applications in the healthcare and life sciences fields. It enables advanced imaging techniques, such as fluorescence microscopy, allowing for detailed cellular imaging and analysis. Embedded vision also facilitates patient monitoring, dermatoscopy for skin condition assessment, and eye diagnosis for ophthalmology applications.
Embedded Vision Cameras from TechNexion
TechNexion is a pioneer in embedded computing solutions, including embedded cameras. Our embedded vision solutions provide powerful capabilities for a variety of industries and applications. They include camera modules, system on modules, panel computing solutions, and more.
With TechNexion’s embedded vision solutions, engineers can achieve real-time decision-making, enhance automation, and enable advanced functionalities such as object recognition, navigation, and surveillance by leveraging on-device processing. This is advantageous, especially in industries such as manufacturing, robotics, healthcare, and smart cities.
Related Products
- What is Machine Vision?
- What is Embedded Vision?
- Embedded Vision vs. Machine Vision
- Applications of Machine Vision
- Quality Inspection
- Assembly Verification
- Measurement and Metrology
- Robotics and Automation
- Applications of Embedded Vision
- Smart Traffic Management
- Robotics
- Precision Agriculture and Vertical Farming
- Smart City Solutions
- Healthcare and Life Sciences
- Embedded Vision Cameras from TechNexion
- Related Products
Get a Quote
Fill out the details below and one of our representatives will contact you shortly.