White balancing is the process of adjusting colors in your images to ensure that they look natural and accurate. Without proper white balancing, photos and videos can appear discolored, with unnatural tints that skew the viewer’s perception of the scene. In embedded cameras, this challenge is even greater due to varying lighting conditions and environments.
For example, consider an embedded camera used in a retail setting. Here, it needs to capture product images under different types of artificial lighting throughout the day. Without proper white balancing, the colors of the products might appear inconsistent. This inconsistency can make it difficult for the AI systems analyzing these images to accurately identify and categorize products.
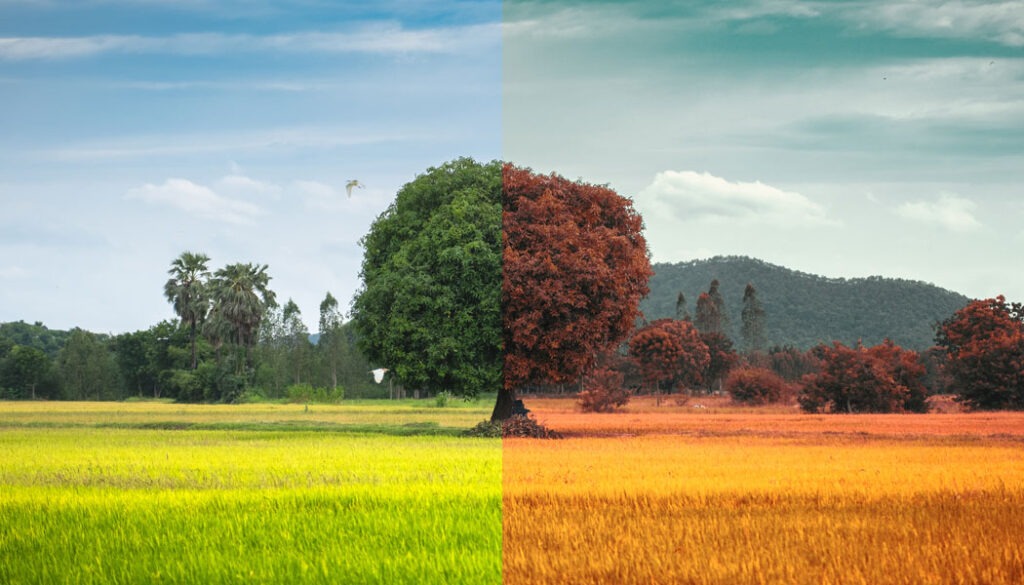

This, in turn, can lead to potential errors in inventory management or automated checkout processes. Achieving precise white balance ensures that the colors remain true to life. This can enhance the effectiveness of image analysis and improve overall accuracy.
Understanding Color Temperature
Before we understand and adjust for white balance, it’s essential to grasp the concept of color temperature. Color temperature measures the warmth or coolness of light emitted by a source, expressed in Kelvin (K). This measurement directly influences how colors are perceived in photographs and videos.
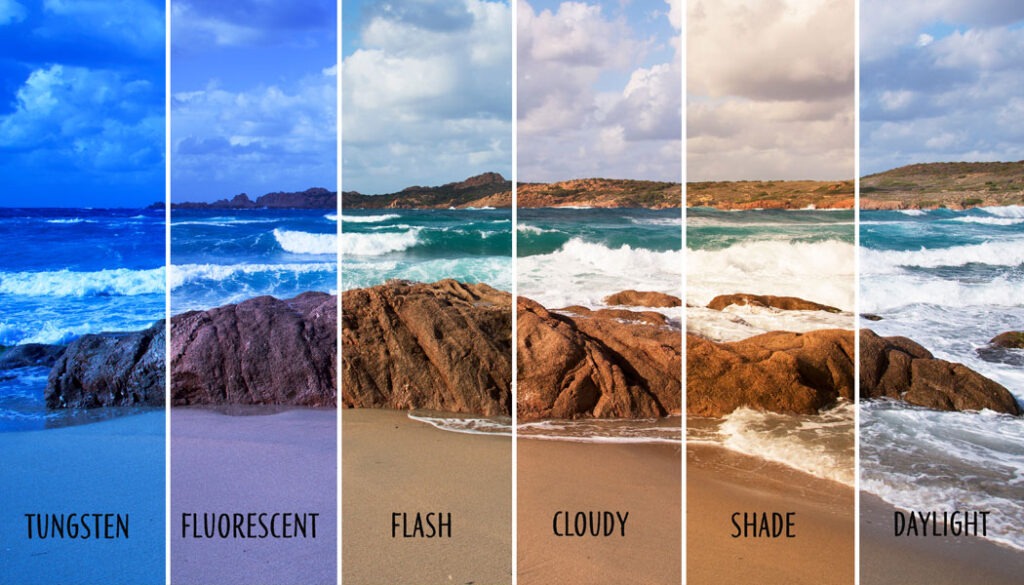

Different color tints
Light sources with lower color temperatures, such as incandescent bulbs, typically emit a warm, yellowish light around 2700K. This warm light can cause white objects to appear more yellow or orange in images. On the other hand, light sources with higher color temperatures, like daylight or certain LEDs, emit a cooler, bluish light ranging from 5000K to 6500K. This cooler light can make images appear bluish.
Understanding color temperature is crucial for effective white balancing. The goal is to adjust the camera’s settings to neutralize the color casts introduced by different light sources. This ensures that white objects look white and other colors appear accurate.
Understanding White Balancing in Detail
Now, that we have understood color temperature, let’s take a look at white balance. White balance is a fundamental aspect of photography and videography, essential for achieving accurate color representation in images. Its primary purpose is to ensure that white objects appear white, regardless of the light source.
This, in turn, ensures that all other colors are also rendered accurately. Without proper white balance, these color casts can distort the color accuracy in embedded vision cameras.
This can hamper the machine vision system’s ability to accurately interpret and analyze colors. The final result will be significant errors in object recognition, quality control, and automated processes.
White balance adjustments correct these color imbalances by shifting the colors in the image so that white appears white and other colors appear natural. Most embedded vision cameras have Automatic White Balance (AWB) settings that can adjust for different lighting conditions.
How White Balancing Works in Embedded Cameras
Embedded cameras often face varied lighting environments, which can complicate achieving accurate white balance. To address this, these cameras typically use a combination of sensors and algorithms.
The camera’s sensors measure the color temperature of the light in the scene. It basically detects how warm or cool it is. Based on this measurement, the camera’s white balance algorithm adjusts the image to neutralize color casts.
There are two primary types of white-balancing methods: automatic and manual. Automatic White Balance (AWB) algorithms continuously adjust the white balance based on real-time analysis of the scene. This makes the camera suitable for dynamic lighting conditions. These algorithms analyze the image to identify areas that should be white and adjust the color channels accordingly.
Manual white balance, on the other hand, involves setting specific white balance parameters based on the lighting conditions of the environment. This method allows for more precise control. This is especially helpful in complex or controlled lighting situations.
Key Factors Affecting White Balance
Here are the primary factors affecting white balance:
Color Temperature
As seen earlier, different light sources emit light at varying color temperatures. Incandescent bulbs typically emit a warm, yellowish light around 2700K. On the contrary, daylight can range from 5000K to 6500K, providing a cooler, more neutral light. This variation affects how colors are perceived by the camera.
Type of Light Source
Fluorescent lights, halogen lamps, and LEDs each have distinct spectral characteristics. Fluorescent lights can introduce a greenish or bluish tint, while halogen lamps produce a more neutral light similar to daylight. LEDs may vary significantly in color temperature based on their design and settings.
Sensor Sensitivity
The sensitivity of the camera’s sensor to different wavelengths of light can impact white balance. Sensors with broader spectral sensitivity may better capture the nuances of different lighting conditions.
White Balance Algorithms
The effectiveness of white balance relies on the camera’s algorithms, which analyze the image and adjust color channels to correct color casts. High-quality algorithms can more accurately compensate for different light sources, while lower-quality algorithms may struggle with complex lighting conditions.
Environmental Factors
The surrounding lighting in the environment can influence the accuracy of white balance. For example, mixed lighting conditions, where natural and artificial lights blend, can create challenges for the camera to achieve correct color balance.
Moreover, surfaces that reflect or scatter light, such as walls or floors, can affect how light interacts with the camera’s sensor. These reflections can introduce unwanted color casts or distortions in the captured image.
Subject and Scene Characteristics
The color and material of the subject being photographed can influence white balance. For instance, a predominantly white scene may require different adjustments compared to a scene with various colors and textures.
Additionally, the distribution and intensity of light within the scene can affect how white balance is applied. Scenes with uneven lighting may require additional adjustments to maintain color accuracy.
Techniques for Achieving Accurate White Balance
Here are some effective techniques for managing white balance:
Use High-quality Cameras
High-quality cameras are equipped with advanced technology that enhances white balance accuracy. These cameras often feature:
Advanced Sensors: High-end cameras, such as the ones offered by TechNexion, come with sensors that have superior color sensitivity and accuracy. These sensors can better measure the color temperature of various light sources, helping to achieve more precise white balance.
Manual White Balance Controls: Some cameras offer manual white balance settings. This feature allows users to calibrate the camera based on specific lighting conditions, offering greater control over color accuracy. By setting a custom white balance, you can correct color casts more effectively than relying on automatic settings alone.
High Dynamic Range (HDR) Imaging: Some high-end cameras, such as TechNexion’s VCI-AR0822-CB, support HDR imaging. This helps capture multiple exposures to provide a broader range of colors and light intensities. This capability helps achieve a more accurate white balance by compensating for varying lighting conditions within a scene.
Leverage Advanced White Balance Algorithms
High-quality white balance algorithms play a crucial role in processing images accurately. These algorithms adjust color channels based on real-time scene analysis:
Automatic White Balance (AWB) Algorithms: Modern cameras and embedded vision systems use sophisticated AWB algorithms to detect and adjust for different lighting conditions. These algorithms analyze the image to identify areas that should be white. They correct color casts by adjusting the red, green, and blue channels. Advanced AWB algorithms are designed to handle complex lighting scenarios, providing more accurate results.
Calibration and Profiling: Many high-quality algorithms include calibration and profiling features. These techniques involve adjusting the camera’s response to different light sources based on standard white references. Calibration ensures that colors remain consistent and accurate, regardless of lighting conditions.
TechNexion - Embedded Vision Cameras for Perfect White Balancing
TechNexion offers a range of embedded vision cameras designed to deliver exceptional White Balance. Our advanced modules leverage high-quality sensors to ensure that every image reflects real White Balance. With features like HDR, low-light enhancement, and near IR capabilities, TechNexion’s cameras excel in capturing accurate and vibrant images in any lighting condition.
Whether you’re employing our cameras for industrial inspection, retail analytics, or autonomous shopping applications, our solutions are engineered to meet the highest standards. Get in touch with us to discover how TechNexion can enhance your imaging capabilities and provide you with the perfect solution for your needs.
Related Products
Get a Quote
Fill out the details below and one of our representatives will contact you shortly.